Artikel Ini Telah Direview Oleh:

Syavin Pristiwayuning
Penulis Makalah Ilmiah Perikanan
Cultivating or raising vannamei shrimp in concrete ponds is one of the top choices because it has many advantages, such as easy maintenance of shrimp and easy control of the environment in aquaculture ponds. One of the well-known vannamei shrimp farming systems in concrete ponds, namely VITON.
However, the cultivation of vannamei shrimp in concrete ponds requires a number of things that must be considered so that the cultivation carried out is maximized. Ladies and gentlemen who are interested in cultivating VITON can read this article to the end, because this article will thoroughly discuss the management and analysis of VITON cultivation.
Come on, see below!
What is VITON?
VITON (Intensive Vaname in Concrete Tanks) is an intensive process of cultivating vannamei shrimp carried out in concrete tanks. Currently, VITON is used as an alternative shrimp farming strategy.
The material in this concrete pool is cement, so this pool is not easily collapsed or damaged. In addition, concrete ponds have a relatively longer life and are not easily eroded by water, so it can be said that concrete ponds tend to be more durable than other shrimp farming ponds. Not only that, VITON can be used as a long-term investment, and is considered to be more effective, efficient and inexpensive.
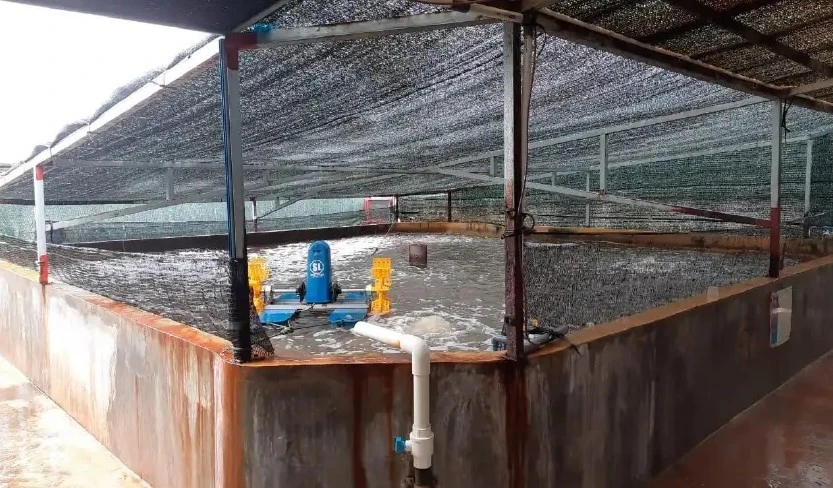

Following are the advantages of shrimp farming in concrete ponds, including:
- Eliminating Soil Porosity
The use of concrete tanks as shrimp ponds can reduce land subsidence due to water pressure. This is because the cement used to make concrete tanks fills the cavities or pores of the soil.
- Breaking Soil Interaction with Aquaculture Water
The use of concrete tanks in vaname shrimp cultivation can minimize water quality problems. The reason is, if you use an earthen pool, you need to pay special attention to the condition of the soil.
The use of earthen ponds can result in the accumulation of organic matter during cultivation, thus possibly causing problems in the next shrimp farming cycle.
- Simplify Water Quality Processing
By using a concrete tub, pond conditions will be more controlled, making it easier for you to manage water quality.
- Facilitate Sterilization
Sterilization in concrete tanks is considered easier because it has a flat surface. In addition, using a concrete tub can minimize pests originating from the ground.
- Shortens Pond Drying Time
By using a concrete pool, the pool drying process will be faster. The reason is, if you use an earthen pond, the time needed for the drying process is relatively long, because before this process you need to do the plowing of the land first.
- Easy Maintenance and Long Lasting
Shrimp ponds with concrete tanks have easier maintenance and are more durable, because concrete ponds have a high capacity to accommodate loads and withstand high and low temperatures.

Behind the many advantages of using a concrete pool, there are several challenges that you should be aware of, including:
- Additional Investment Costs
Concrete tubs have strong and durable resistance, therefore you need to increase investment costs. However, when reviewed, the investment costs that you spend are proportional to the durability and duration of use for shrimp farming.
- It is necessary to pay attention to the condition of the concrete pool
Concrete pools have high resistance, but this pool also has a weakness, namely if it is hit by an earthquake it will cause cracks in the pond. So, you need to check regularly.
- Routine Water Quality Checks
You need to check the quality of the water regularly, this is because dirt, leftover feed, and organic matter in shrimp farming ponds are toxic.
You need to pay attention to feeding, if the remaining feed in concrete tubs accumulates it will cause decay in the culture water, thereby reducing the quality of pond water and becoming a breeding ground for disease.
You are advised to always maintain water quality, such as DO. The recommended oxygen level for shrimp farming in concrete tanks is at least 4 mg/l. In addition, you are advised to add a water wheel to the concrete pool to maintain oxygen levels.
Management of VITON Vaname Shrimp Cultivation
In the cultivation of vannamei shrimp in concrete ponds, there are several managements that need to be carried out, such as:
1. Management Nursery

Nursery or nursery is a way that has long been known by farmers in Indonesia. Technology nursery produce seeds with better digestive systems and adaptability.
Another benefit is that it can reduce the risk of fry mortality and reduce the spread of disease. Not only that, seed selection will also be more effective, so that only quality seeds are used for cultivation.
Some of the main components of utilization nursery as a supporter of VITON production, including:
- Nutritional intake right in the initial phase of maintenance.
- Biosecurity.
- Control water management, feed and shrimp health.
However, in utilization nursery There are several things to note, as follows:
- Efforts are made to stocking density and maintenance time not to reduce the growth performance of vannamei shrimp.
- Location nursery must be close to the enlargement location to reduce the risk of stress on vannamei shrimp.
Management nursery divided into water management, feed management, and shrimp health. The main water quality parameters are the availability of a minimum DO of 5 ppm and a pH of 7.5-8.
In addition to water management, you also need to manage feed and shrimp health. By providing feed that is in accordance with the amount with nutrition, it will make the health and growth of shrimp optimal.
You also need to pay attention to the stocking density, you can sow seeds with a density of 6000-9000 PL/m³ with an initial seed weight of around 0.01-0.03 gram.
In addition, you need to review production management and carrying capacity environment during the maintenance period until finally getting seeds of the desired size.
You also need to minimize the potential for stress due to shrimp handling and acclimatization of the seeds when they are put into the rearing tub. If you don't pay attention to this, it is possible that the seeds will die due to the stress experienced.
2. Maintenance Management

In the management of raising shrimp in concrete tanks, you need to do important things in the VITON system, such as pond preparation, water preparation, seed stocking, maintenance, checking water quality and disease, and harvesting.
Here's how to cultivate vannamei shrimp in concrete pools, including:
- Concrete Pool Preparation
The initial stage in cultivating concrete tubs is preparing a pond or concrete tub. You can adjust the size of the pool used according to the existing land.
After preparing the pool, you should check the condition of the pool. You can check whether the pool has a leak or not. In addition, you can check for residual dirt from the previous cycle attached to the concrete pool wall.
You can clean the dirt on the pool walls with soap. After that, you need to do calcification at the bottom of the pond to prevent harmful biotic elements and pests.
- Water Preparation
After you have done the pool preparation, you also need to do the water preparation, starting from the sterilization stage to water formation.
The sterilization stage aims to kill microorganisms in the pond, the presence of microorganisms is feared to interfere with the cultivation process. At this stage, you can use chlorine, TCCA, H2O2, saponins, cupric sulfate, and others.
Then, the water formation stage is used to revive microorganisms such as plankton or bacteria, this aims to support the cultivation process.
- Seed Spreading

After you have prepared the water and checked the water quality, you can carefully stock the fry. You can put vannamei shrimp seeds with PL 9 – PL 11 sizes. In addition, you need to make sure the vannamei shrimp have a uniform size so that cannibalism does not occur.
The stages of spreading fry can be done in the following way:
- Check fry resistance with stress test
- Disease check
- Sampling fry for the determination of feed and stocking density
- Fry acclimatization by soaking a plastic bag filled with fry, then wait a few moments for it to condense. After that, you can open the plastic bag and wait for the fry to come out by themselves.
- Maintenance
Basically, the maintenance of VITON vannamei shrimp is the same principle as shrimp farming in ponds. The maintenance process carried out includes:
- Feed management to determine the right amount, time, frequency of species, size and quality of feed according to age stage
- Regular and continuous water quality management
- Giving feed additives to prevent disease
- Administration of probiotics or fermented water
- Calcification of water to grow plankton or mineral supply for shrimp when molting
- Shrimp sampling to determine the condition of the shrimp
- Intensive pond bottom monitoring and management
- The stocking density of fry is adjusted based on the specifications of the applied technology
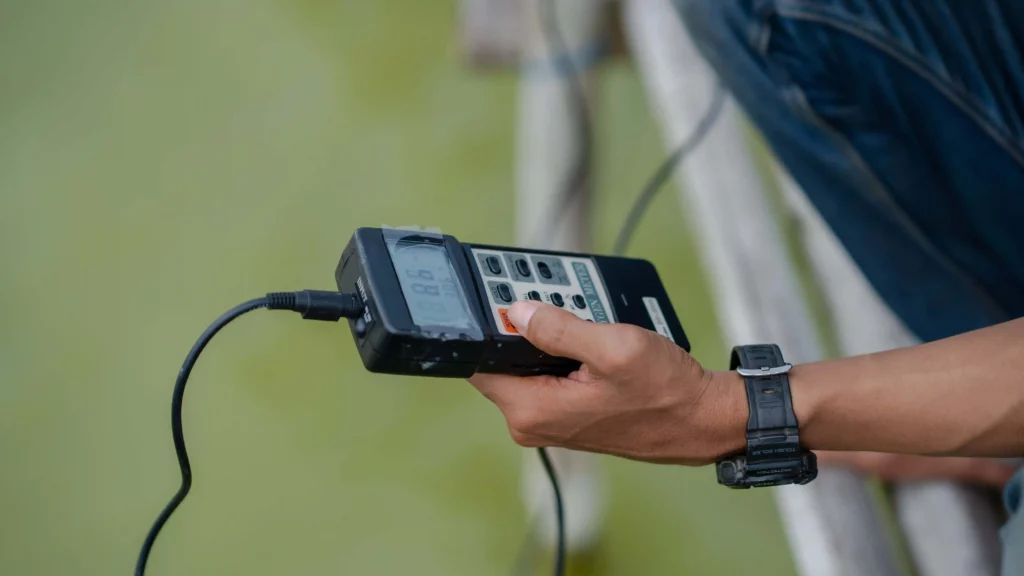
- Checking Water Quality and Disease
After you do maintenance, you need to check water quality and disease, the results of these measurements can be used to determine the condition of the waters and the health condition of the shrimp.
Concrete pond water for cultivation must have good water quality. The following is a range of optimal water quality parameters for vannamei shrimp ponds:
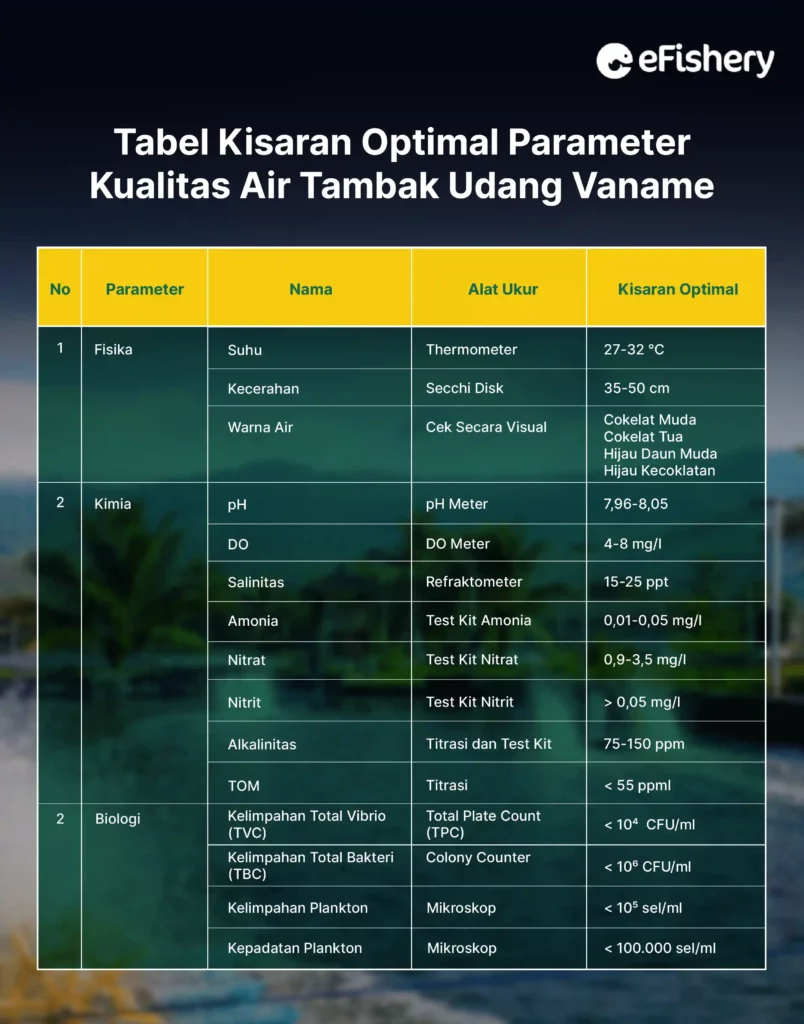
In checking for disease, you first need to do sampling with anco to monitor the health of the shrimp so that it is always maintained. Disease checks can be done daily, weekly, or as needed.
3. Harvest
Harvest is the goal to get results from cultivation. The harvesting process is carried out when the shrimp have reached the maximum cultivation limit and have high economic value.
Generally, vannamei shrimp can be harvested when they are 110-130 days old. Because at that age the growth of shrimp can no longer be maximized. Then, at that age the shrimp is estimated to reach a size of 40 heads/kg.
However, if the capacity of the concrete tank pond is almost to the maximum limit, it is usually done with a partial harvest first to avoid increasing shrimp mortality due to lack of oxygen.
Analysis of VITON Vaname Shrimp Cultivation Business
In conducting the VITON vannamei shrimp farming business, you need to know the estimated analysis of the cultivation. An example is the case study of a shrimp farmer in Serang, Banten in 2022, the bottom of the pond used is concrete while the walls of the pond are covered with 0.5 mm HDPE plastic. This is useful for saving pond construction costs. Here is the business analysis:
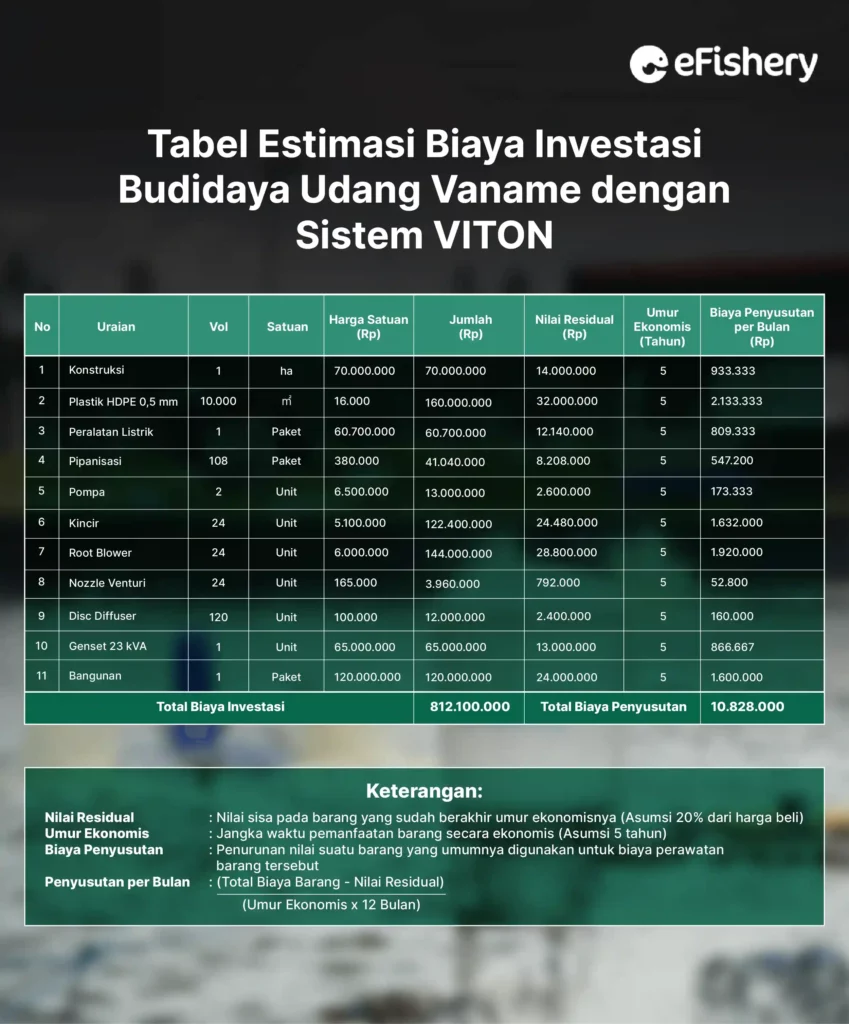
From the table, the total investment cost of VITON shrimp farming is IDR 812,100,000 with the total depreciation expense being IDR 10,828,000 per month. After knowing the estimated investment costs, you need to know the estimated costs per cycle. Come on, see below!
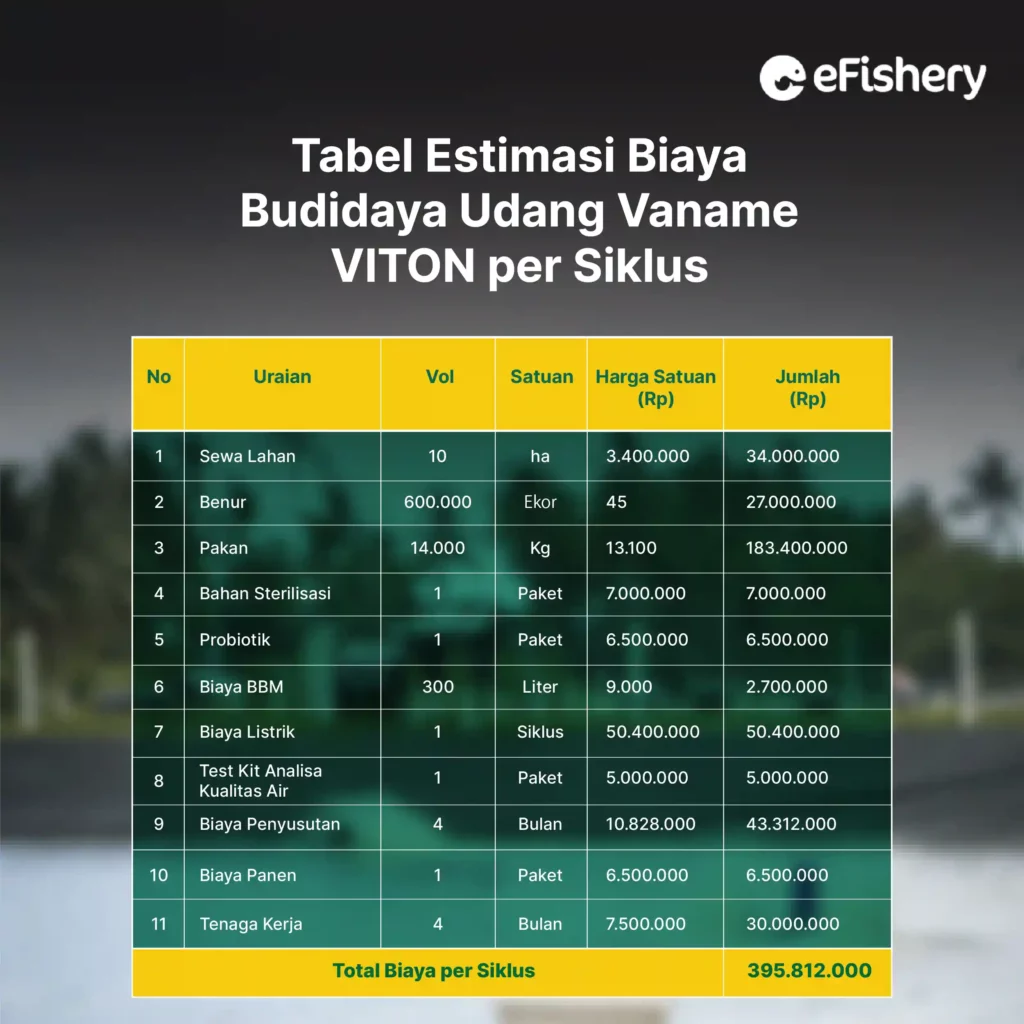
From the table above, the total cost per cycle incurred for VITON vannamei shrimp farming is IDR 395,812,000.
After knowing the costs of vaname VITON shrimp farming for 1 cycle, the following is the calculation of the estimated profit and loss analysis of vanname VITON shrimp farming:
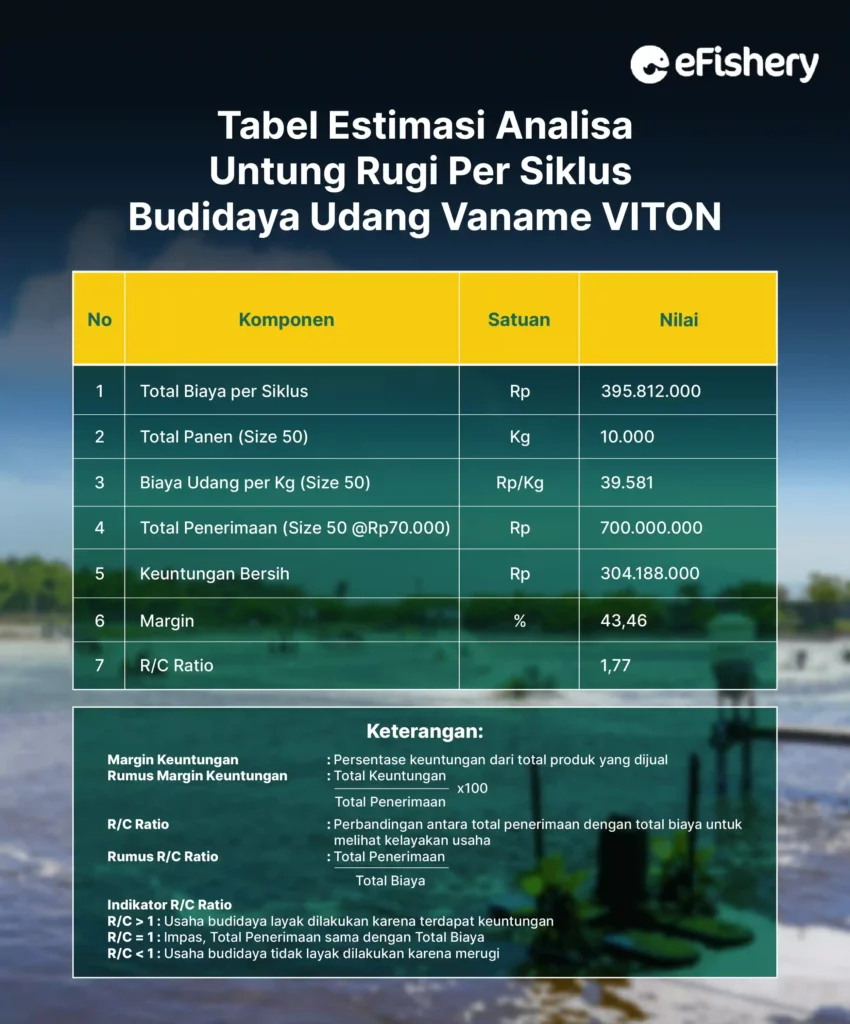
Of the total cost per cycle issued by IDR 395,812,000, Farmers can get revenue of IDR 700,000,000 with a huge profit IDR 304,188,000.
The cost to produce shrimp size 50 per kg is equal to IDR 39,581. This cost figure can be used by farmers as a reference for determining the selling price of shrimp per kg, which of course is adjusted to market prices in order to get optimal profits.
The profit margin obtained from Farmers in VITON shrimp cultivation is as much as 43,46%. This shows that farmers are able to get a profit of 43,46% from the total revenue, where the remaining 56,54% is used for costs during cultivation.
Furthermore, the R/C ratio shows a number 1,77 which means that this cultivation business is feasible because the total revenue is greater than the total cost where every Rp. 1 spent will provide revenue of Rp. 1.77 and a profit of Rp. 0.77.
Cultivating vaname shrimp in concrete ponds is very profitable, isn't it? The estimated calculation may change according to pond conditions and the number of fry to be cultivated. In addition, if you add other tools, of course the monthly costs that you spend will be higher.
Learn More about Shrimp Farm Management at eFarm!
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
Cultivating shrimp using concrete tubs will be very profitable if you take it seriously and apply good and correct cultivation management. For this reason, you need to complete various information on shrimp farming.
However, have you ever had trouble finding reliable and trustworthy information about shrimp farming?
With so many hoaxes circulating on the internet, you don't need to worry anymore about finding information, because there are eFarm! You can get various knowledge about Aquaculture in features Learn Cultivation. eFarm provide various solutions to the problems of shrimp farming that you are currently working on.
In addition to getting information about cultivation, you can consult directly with aquaculture experts who can help with your various cultivation problems.
Take advantage of features Learn Cultivation for FREE only in eFarm!

Syavin Pristiwayuning - Penulis Makalah Ilmiah Perikanan
Berpengalaman sebagai asisten koordinator pelatihan teknisi pada tahun 2020 dan saat ini aktif sebagai Technical Support Online di eFishery
- Andriyanto F, Efani A, and Riniwati H. 2013. Analysis of Production Factors in Vannamei Shrimp Growing Business (Litopenaeus vannamei) in Paciran District, Lamongan Regency, East Java; The COBB-Douglas Function Approach. ECSOFiM Journal. 1(1): 82-96
- Dervish SW. 2018. Vaname Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Maintenance Management at PT. Esaputli Main Initiative (benur Kita) Barru Regency, South Sulawesi. Thesis. Fisheries Agribusiness Study Program. 50 pp.
- Novriadi R. 2020. Intensive Vannamei Shrimp Production in Concrete Tubs (VITON). 38 p.
- Supono. 2018. Water Quality Management for Shrimp Farming. Main Grace Award. 132 pp.
