Artikel Ini Telah Direview Oleh:

Muhammad Mustofa
Praktisi Budidaya Udang
In shrimp cultivation, vannamei shrimp hatchery is one of the determining factors for the success of cultivation. You need to pay attention to the vannamei shrimp nursery to get maximum cultivation results. You need to pay attention to the vannamei shrimp breeding method to get superior and best quality shrimp seeds.
Vannamei shrimp breeding techniques start from selecting vaname shrimp broodstock, rearing, spawning, hatching eggs, to caring for the larvae. For that, see this article and get the most complete information about the right vannamei shrimp breeding!
Technical and Non-Technical Requirements for Vaname Shrimp Hatchery
In the shrimp farming business, hatchery is a crucial factor that must be done properly in order to produce superior and quality vannamei shrimp seeds. Thus, there are several technical and non-technical factors so that the vannamei shrimp hatchery is maximized. Some of the factors in question are:
1. Vaname Shrimp Hatchery Technical Requirements
a. Water sources
The source of water in the hatchery greatly determines the larvae produced. There are several aspects of water sources that need to be observed, including:
- Free from pollution and heavy metal deposits
- It has a relatively low organic matter content
- Salinity ranges from 15-25 ppt
- The pH of the water ranges from 7.96-8.05
- Availability of fresh water is sufficient and easy to obtain
b. Environment
A good environment is one of the requirements for the vannamei shrimp hatchery technique. A polluted environment will cause the condition of the shrimp to decline, making it susceptible to disease. There are several environmental aspects that need to be considered when hatching shrimp, such as:
- Disposal on hatchery can dispose of nutrient-rich waste.
- The environment is not an intermediary for disease transmission in shrimp
- Hatchery areas are not areas prone to conflicts of community interest
c. Facilities and infrastructure
Facilities and infrastructure are one of the supporting factors for the vannamei shrimp hatchery process. The following are the facilities and infrastructure that must exist at the hatchery location, including:
- Laboratory room, drug storage, equipment storage, as well as office or administration room.
- Settling tanks or containers, filtration systems and reservoirs, quarantine containers, spawning containers, hatching containers, and waste management
- Production and harvest equipment, as well as laboratory equipment
- Means biosecurity between production units and completeness of personnel
2. Non-technical requirements for hatching Vaname Shrimp
Non-technical requirements are a complement and support for technical requirements in the success of vaname shrimp hatchery activities through facilities and infrastructure. The non-technical requirements for vannamei shrimp hatchery are:
- Means of Transportation
- Electrical installation
- Communication
- Health services
Vaname Shrimp Hatchery Technique
If you are interested in the vannamei shrimp hatchery business, you need to understand the basic hatchery techniques first. The reason is, to produce quality shrimp fry, you need a good and correct hatchery process.
You need to pay attention to water quality management, feeding, brood spawning, and hatching of vannamei shrimp eggs. The vannamei shrimp hatchery technique consists of 3 stages, including:
1. Pre Production of Vaname Shrimp Hatchery
a. Container Preparation
You need to clean the vaname shrimp cultivation container using a disinfectant to remove dirt that sticks to the walls and bottom of the pond. There are several types of shrimp farming containers depending on their functions, such as brood spawning containers, egg handling, larva rearing, and feed storage.
b. Media Preparation
After preparing the container, the next step is to stock up on seawater to be used. Seawater for vannamei shrimp should have water quality parameters, as follows:
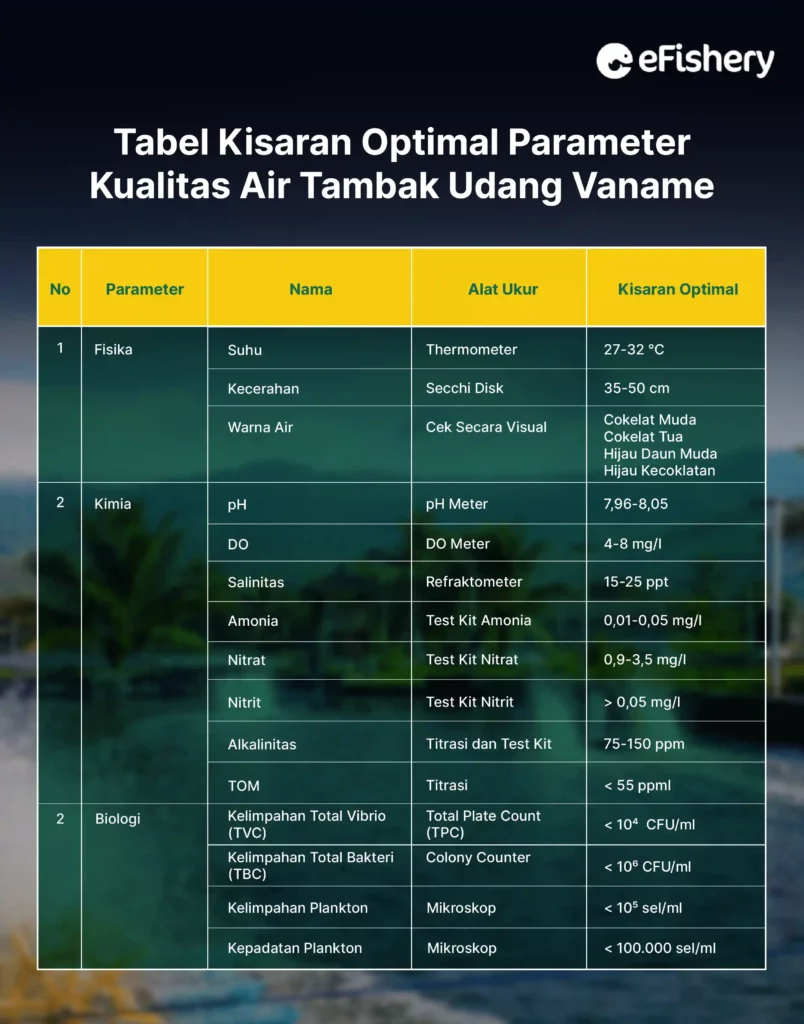
In the process of sterilizing seawater for aquaculture, you need a pump filter and a water distribution installation. Then, the height of the water to be taken for cultivation is at least 80 cm from sea level, provided it is not muddy. After that, you can sterilize it with chlorine to kill bacteria in seawater that will be used for cultivation.
2. Vaname Shrimp Hatchery Production
a. Master Procurement
In procuring broodstock, you need to choose healthy and quality broodstock to get the best quality fry. For this reason, you need to know the characteristics of quality vaname shrimp broodstock, including:
- Parent age is ripe, at least 7-8 months old
- Parent must be SPF certified (Specific Pathogen Free) and SPR (Specific Pathogen Resistant) in order to avoid pathogens that cause disease in shrimp
- The size of the parent shrimp is uniform, shrimp that are small indicates that their growth is stunted
- Body shape is complete and not defective, you need to ensure that the eyes, antennae, legs and tail of the shrimp are in complete condition and are not defective
- The intestines of vannamei shrimp are filled, this indicates that the appetite of the shrimp is large so that the growth and development of the shrimp is relatively good
To get superior vannamei shrimp seeds, you must use quality broodstock. For this reason, the first step that needs to be taken is to select the parent vannamei shrimp.
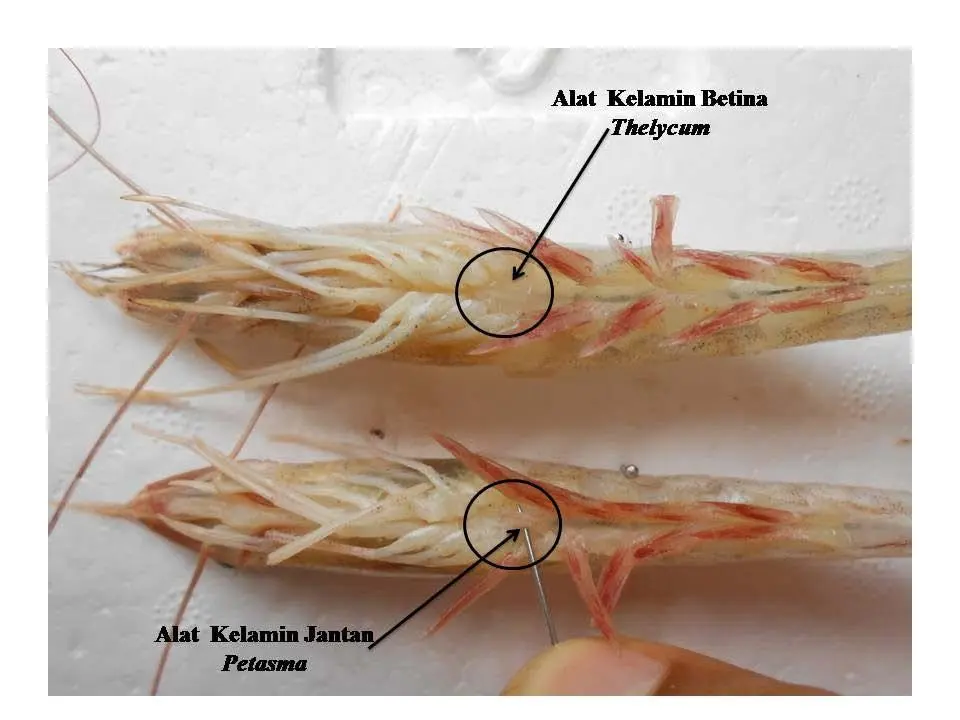
The criteria or requirements for quality shrimp brooders are as follows:
- Heavy: 60-80 gram (male) and >80 gram (female)
- Body Length: 18-20 cm (male parent) and 20-25 cm (female parent)
- Sex: clean
- Gill: normal and red in color with a transparent cover
- Limb: complete and normal
b. Handling of Main Vaname Shrimp
The process of caring for male and female parents must be carried out in separate places. The maintenance site used is a concrete pond with a depth of 80-100 cm. Stocking density in rearing tanks ranged from 1-4 fish/㎡. This is to avoid the occurrence of cannibalism in the parent being kept.
Parental maintenance of vannamei shrimp, includes ablation techniques and TKG (Gonad Maturity Level) measurements. The ablation technique in shrimp is used to accelerate the maturation of female parent gonads. Eye ablation is done by removing the X-Organ on the eye stalk of the shrimp cautery (massaging the eye stalks of the shrimp) and cutting (cutting the eyes of the shrimp).

Meanwhile, TKG measurements were carried out based on the development of the ovary (shrimp back), starting from the initial segment to the base of the shrimp tail. The more mature the gonads, the ovaries will thicken and change color from white to yellowish red.

c. Broodstock Management
Feed is one of the keys in the development of vannamei shrimp gonads. In this rearing process, vannamei shrimp require feed in the form of pellets as much as 10-45% of their body weight with a protein content composition of 30% and a frequency of 4-6 times/day.
Apart from pellets, you can also provide fresh feed which contains sufficient protein and vitamins, so that it can maintain the body's resistance to disease, and increase the growth and development of the gonads.
The following is the amount of fresh feed that you can give to the broodstock:

d. Parent Spawning
Spawning is the release of eggs by the female shrimp followed by fertilization of sperm from spermatophore which exist in telicum female parent. For Mr / Mrs Farmers who are going to spawn vannamei shrimp, it is necessary to recognize the signs of broodstock that have undergone gonad maturation.
The maturity level of the eggs is measured based on the development of the ovaries which are located on the back of the shrimp. The ovaries on the back of the shrimp are green, the more mature the ovaries are, the darker the color and will look wider and grow towards the head. Gonad Maturity Level (TKG) of female shrimp broodstock, as follows:
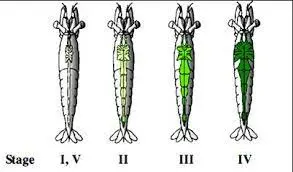

From the table above, it can be concluded that the TKG on female shrimp brooders is when they have entered the TKG III phase. Meanwhile for male shrimp, gonadal maturity can be seen from the development of perfect petasma and usually contain spermatophora.
Spawning usually begins with the molting of the female parent's skin, then the mating process begins when the parent shrimp returns to its normal state. Spawned male and female vannamei shrimp have a ratio of 2:3 or 1:2.
Shrimp spawning process can last for 4-5 hours. After the spawning process, you need to separate the eggs from the brood shrimp, then carefully put the shrimp eggs into the hatchery pond.
e. Egg Handling
Shrimp eggs will hatch within 10-12 hours. In hatching eggs, it is necessary to provide aeration and stir the eggs manually with a frequency of 15 minutes so that the eggs float on the surface of the water, because the eggs that settle to the bottom of the hatchery will be easily attacked by fungus.
f. Harvesting Naupli
Eggs in the hatching tank will develop into naupli. Harvested naupli should reach stage 4 (N2). Naupli harvesting is carried out in stages by waiting for the naupli to float on the surface of the tub.
g. Larvae Care
Vaname shrimp larvae need to be treated in separate tanks. You need to provide feed that is adjusted to the size of the larva's mouth. After 3 days of hatching, the shrimp larvae can be given artemia as natural food every three hours.
During the larval treatment phase, you need to maintain salinity in the range of 15-25 ppt. Water change also needs to be done by replacing it as much as 25-50% of the total amount of water in the larvae treatment tub.
Larval rearing is carried out for 15 days or PL 10. You need to adjust the stocking density to the dimensions of the rearing container, this is so that the shrimp grow optimally.
h. Feed Management

Feed is an important thing that needs to be considered in the maintenance of vannamei shrimp larvae. Vaname feed management, consisting of the type of feed used, the dose of feed given, the time of feeding, the frequency of feeding, and the method of feeding for vannamei shrimp larvae.
The feed given is in the form of natural feed and artificial feed. Natural food was given for the first time at the beginning of rearing (stage N6-M3) in the form of nutritious microalgae. Meanwhile, the pattern of rearing larvae at the end of the stadia (M3-PL10), can be given zooplankton (Artemia salina) which has protein 54,60% to support growth.
In addition to natural food, you need to provide artificial feed with protein content ranging from 20-70% and carbohydrates 20% to maintain metabolic processes and increase larval growth.
The recommended feed for shrimp must be certified by the Directorate General of Aquaculture (DJPB). In addition, the nutritional content of the larvae must have high nutrition to accelerate their growth.
To maintain the quality of the feed, you need to store it in a place that is free from disturbing animals, such as rats and insects to prevent pathogens from entering the feed.
i. Water Quality Management

Monitoring kualitas air pada budidaya udang vaname perlu dilakukan setiap waktu agar kelangsungan hidup larva udang terjaga hingga panen tiba. Pengelolaan kualitas air dapat Bapak/Ibu lakukan dengan pengukuran parameterer kualitas air, seperti suhu, salinitas, pH, alkalinitas, dan oksigen terlarut (DO).
j. Pest and Disease Management
In aquaculture ponds, there are several pests that are often found, such as wild fish, crabs, and barnacles in holding tanks. Meanwhile, diseases in vannamei shrimp are caused by viruses, fungi, parasites, and bacteria.
There are several ways to prevent shrimp disease that you need to know, here are the effective ways:
- Application of Biosecurity
Biosecurity is a measure to prevent disease from entering the culture system. You can apply biosecurity in a simple way, such as water quality and sanitation management.
- Certified Benur
One of the steps in disease management is to choose superior fry. Fry fry that are certified and free from pathogens are one of the requirements for successful and smooth shrimp farming.
- Administration of Probiotics
Probiotics are good bacteria that can minimize the growth of pathogenic bacteria and increase productivity. Generally, the types of good bacteria that can be given are types of lactobacillus and bacillus.
- Administration of Immunostimulation
Immunostimulants function to increase immunity in shrimp. Giving immunostimulants functions to make shrimp more resistant to disease. The immunostimulant that is usually given to shrimp is vitamin C.
Know Various Techniques Related to Shrimp Cultivation at eFarm!
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
Even if you already know the proper vannamei shrimp hatchery technique, it doesn't mean that you are a farmer without other problems related to shrimp farming. You need to complete information and knowledge about shrimp farming and business opportunities at Learn eFarm Cultivation!
Feature Learn Cultivation will make it easier for you to get help from a professional team to ensure that the cultivation activities that you are currently carrying out run smoothly without any problems.
Learn eFarm Cultivation equipped with educational videos and tutorials, such as shrimp feed management, disease management, how to calculate shrimp farming business capital, and many more.
All the cultivation solutions that you need are in eFarm. come on, downloads eFarm for FREE, right now!

Muhammad Mustofa - Praktisi Budidaya Udang
Berpengalaman sebagai Asisten Dosen Universitas Pekalongan dan kini menjadi Online Technical Capability Development di eFishery
Questions Regarding Vaname Shrimp Hatchery
Vaname shrimp hatchery consists of hatchery pre-production and hatchery production. In the seeding pre-production stage, it consists of container preparation and media preparation.
Meanwhile, the production stage of the vannamei shrimp hatchery consists of broodstock procurement, brood maintenance, broodstock feed management, brood spawning, egg handling, naupli harvesting, larval rearing, feed management, water quality management, and pest and disease management.
- Afrianto A and Muqsith A. 2014. Production Management of Vaname Shrimp Nauplius (Litopenaeus vannamei) At the Shrimp Hatchery Installation of Brackish Water Aquaculture Fishery Center, Gelung, Situbondo, East Java. Brackish Water Cultivation Fishery Center (BPBAP), Situbondo. Journal of Fisheries Science. 5(2): 53-64
- FAO Fisheries Department. 2003. Health Management And Biosecurity Maintenance In White Shrimp (Penaeus Vannamei) Hatcheries In Latin America. Viale Delle Terme Di Caracalla, Italy. 62 p.
- Ministry of Education. 2004. Selection and Maintenance of Shrimp Broods. 35 pp.
- IMI Ismail. 2017. Management of Vaname Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Hatchery PT. Sinar Barru Prima, Barru Regency, South Sulawesi. Thesis. Fisheries Agribusiness Study Program. Pangkep State Agricultural Polytechnic.
- Melmambessy EHP. 2011. First Ripe Size of Shrimp Gonads Penaeus merguiensis De Man (1988) in the Arafura Sea in the Naukenjerai District, Merauke Regency. Agribusiness and Fisheries Scientific Journal (UMMU-Ternate Agrikan). 4(2): 75-81.
- Ramadhanthie R, Kristiany MGE, and Rukmono D. 2020. Technical Analysis of Financial Analysis of Vaname Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Hatchery at CV. Pacific Harvest Shrimp Hatchery, Banyuwangi, East Java. JSJ Newsletter. 2(1): 13-22.
- SNI 7311:2009. 2009. Vaname Shrimp Seed Production (Litopenaeus vannamei) sowing seed class. National Standardization Body, Jakarta.
- Syaifullah. 2020. Vaname Shrimp Hatchery
- tae. S., A. Nawang, & A. Mansyur. (2011). The Effect of Feed Rotation on the Growth of Survivability and Production of Vaname Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei). Research Institute for Brackish Water Aquaculture, South Sulawesi.
