Artikel Ini Telah Direview Oleh:

Eko Afriantoro
Praktisi Budidaya Udang
Pond Preparation and Pond Water Filling
Before starting cultivation, it is necessary to prepare ponds such as drying for ± 1 month, liming, fertilizing, and filling with water. The steps for filling and treating water that must be carried out are as follows:- Sterilize the cultivation plots using a disinfectant such as chlorine. The purpose of water sterilization is to kill harmful pests and disease-carrying pathogens during the cultivation process.
- Add water to the cultivation plot to a minimum height of 100 cm.
- Turn on the waterwheel to increase the dissolved oxygen content in the cultivation plots.
- Spread probiotics such as Lactobacillus sp. 20 ppm for 7 consecutive days.
- If the plankton has not grown, then apply a mixture of ZA and Urea 5 ppm.
- Check the water before stocking fry. The goal is to check the water quality to match the needs of fry.
Pond Water Treatment During Shrimp Cultivation
Water quality management during the cultivation process is one of the determinants of the success of cultivation. This is because water quality plays an important role in supporting the life and growth of shrimp. Thus, good water quality management is needed. The water quality management that can be done is:- Perform water changes gradually according to the age of the shrimp which ranges from 5 – 20% high water.
- Siphon periodically after the shrimp is over DOC 25. The purpose of siphoning is to remove impurities such as faeces and leftover feed at the bottom of the pond.
- Do treatments water such as the addition of probiotics and molasses every 3 days (done alternately). Other than that, it can be done treatments orally or mixed with feed. Purpose of doing treatments water and oral, namely to form a balance in the digestion of shrimp, so that it can suppress harmful pathogenic bacteria. Besides that, treatments This can also be a solution to overcome Plankton is too concentrated.
- Keep the water quality within the optimum range for shrimp rearing and do it immediately treatments when the water quality is not optimal. The following is a table of the optimal range of shrimp pond water quality parameters during the rearing period:
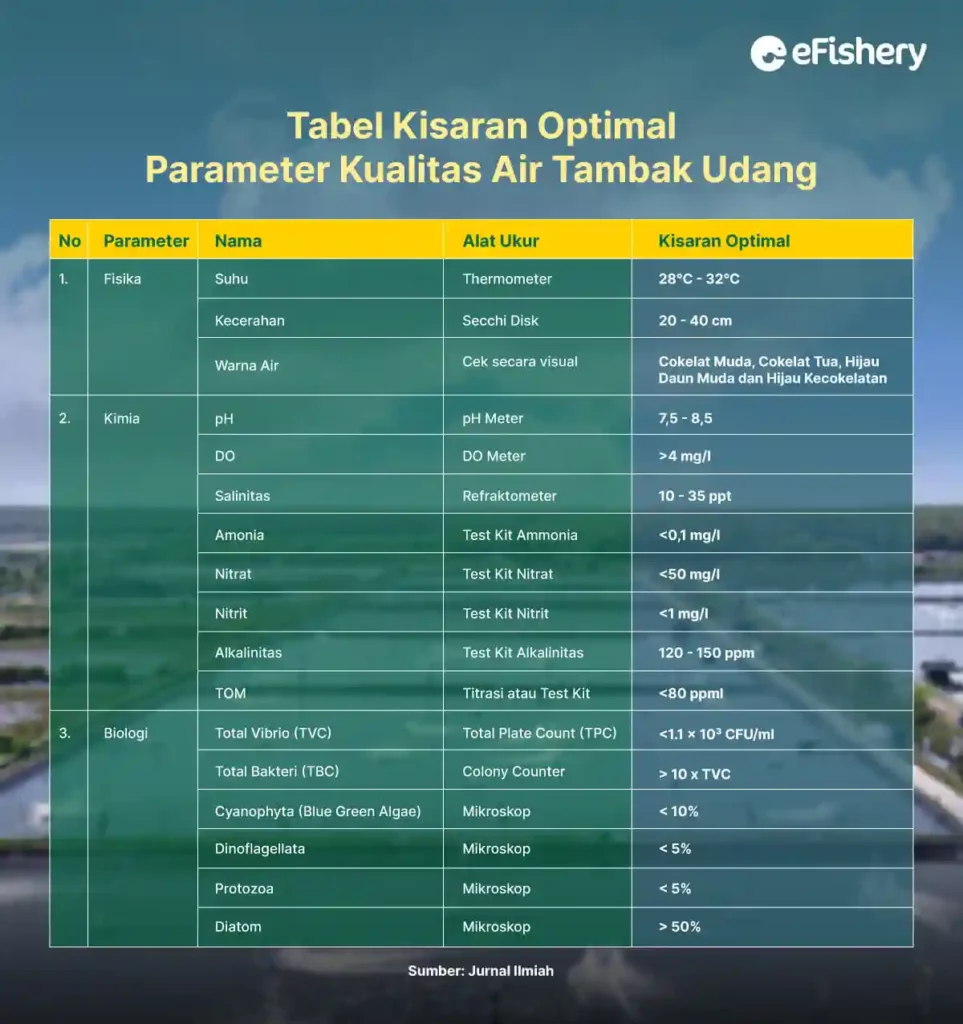
Physics Parameters
Physical parameters include temperature, brightness, and pond water color. Following are some of the common constraints and causes found in each parameter:
1. Temperature
High temperatures can be overcome by maximizing the wheel to avoid coating (blooming) plankton and control feeding strictly according to the estimated SR because the appetite of shrimp at high temperatures will increase. In addition, farmers can also install waring to reduce heat. Meanwhile, low temperatures can be overcome by trying to keep the water not too deep and the plankton more concentrated (25 cm). Plankton also needs to be maintained so it doesn't drop when it rains. In addition, you can maximize the provision of lime if the temperature drops due to heavy rains and reduce feeding because there is a potential for decreased shrimp appetite.2. Brightness
If the water is cloudy and is caused by minerals (brown water), you can fix it by settling particles, filtering the water and adding organic matter. However, if the cloudy water is caused by plankton (greenish water color), then you can do calcification and reduce the use of fertilizers. Meanwhile, if the pond water is clear, you can provide a sufficient source of nutrients to grow plankton and carry out treatments water, such as bran fermentation, to nourish and grow plankton.3. Water Color
Pond water colors that are good and suitable for shrimp farming are light brown, dark brown, light green leaves, and brownish green. If the pond water is a different color, then you can do the following:- If the pond water is greenish brown and yellowish green, then you can dilute the water
- If the pond water is blue brown, reddish brown, dark green, bluish green, then you can do a water change
- If the pond water is reddish brown, then you can give lime and urea fertilizer
- If the pond water is dark green, then you can give dolomite lime (lime that contains magnesium)
- If the pond water is clear blackish brown, then you can do land reclamation
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
Chemical Parameters
Chemical parameters include pH, DO, salinity, ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, alaklinitas, and TOM. Following are some of the common constraints and causes found in each parameter:
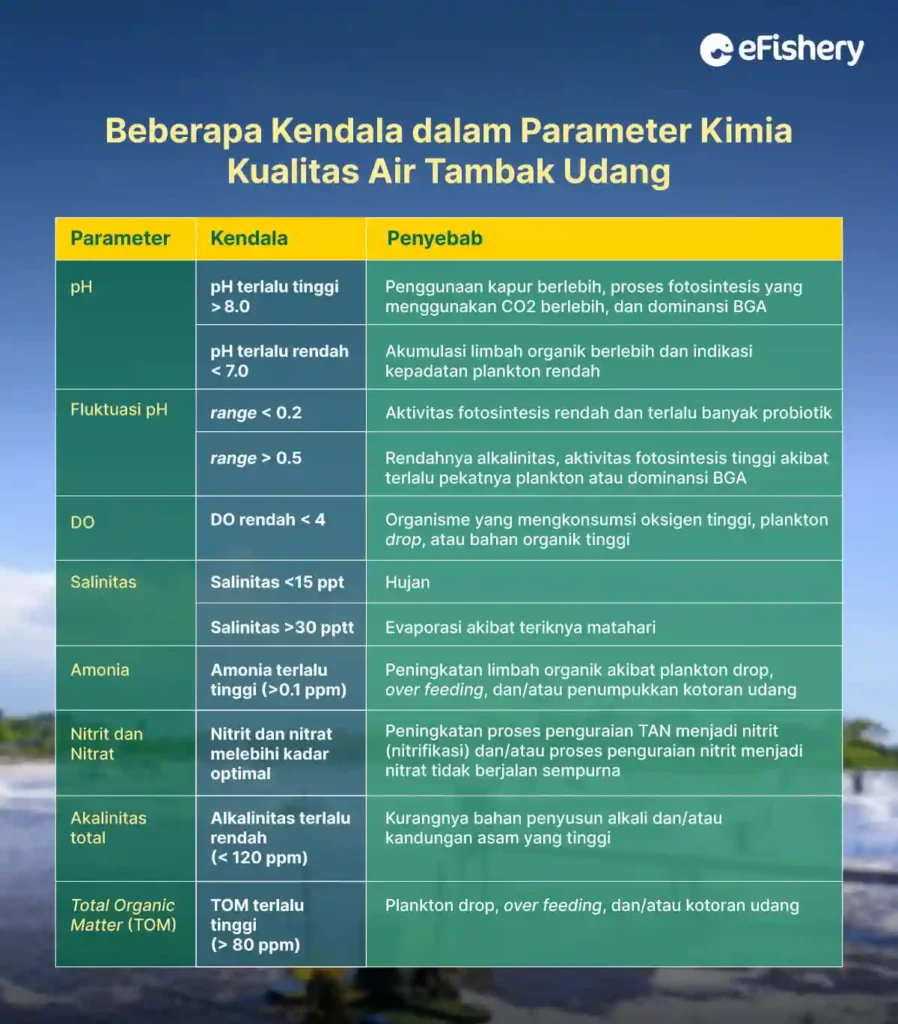
1.pH
pH problems are generally divided into 3, namely:
- pH too high
If the pH is high and there is a drop in plankton, then immediately do a siphon to reduce organic waste. However, if the pH is high and the dominant BGA (Blue Green Algae), then maintain the balance of plankton and try to dominate the brown/diatom plankton.
- pH too low
If the pH is low, then immediately perform a basic siphon and treatments addition of nitrifying bacteria. If the low pH is due to a drop in plankton, immediately perform a basic siphon and maintain the balance of the plankton by adding fertilizer to regrow the plankton.
- pH fluctuation
If the pH fluctuations are still on range pH <0.2, farmers can maximize the operation of the waterwheel, maintain optimal plankton growth, reduce probiotics and probiotic supporting materials (organic materials such as molasses/drops). However, if the pH fluctuations are in the pH range > 0.5 because the plankton is too concentrated, immediately carry out dilution, siphon and captan application.
Meanwhile, if pH fluctuations occur due to the dominance of BGA, then shift the dominance of BGA with diatoms by giving captan in the morning and encouraging the growth of diatoms in the afternoon with low doses of phosphate and nitrate fertilizers every day.
2. DO (Dissolved Oxygen) or Dissolved Oxygen
If DO is low <4, then optimize the wheel and add more wheel. If estimate carrying capacity does not support (shrimp are too dense in 1 pond), then do a partial harvest to reduce shrimp density and check daily feed because there is potential overfeeding and the accumulation of organic matter which results in competition for oxygen in the waters.
3. Salinity
If the salinity is low, remove the fresh water that is on the surface of the pond through a discharge pipe above the water level and increase the salinity slowly by adding sea water.
Meanwhile, if the salinity is high, add fresh water until the water level reaches the initial height before evaporation and you can also replace the water with the addition of fresh water.
4. Ammonia
If the ammonia is too high due to a drop in plankton, immediately do a siphon to get rid of the dead plankton that has settled as soon as possible. Then, add Kaptan 5-10 ppm and spread decomposer probiotics.
If any indication overfeeding, reduce feed and do dilution. However, if the nitrification process is hampered, then you can add nitrifying bacteria.
5. Nitrite and Nitrate
If nitrite and nitrate exceed optimal levels, siphon, reduce feed, dilute, add nitrifying bacteria, and replace water.
6. Alkalinity
If the alkalinity is low due to a lack of lime at the beginning of the pond preparation, then dolomite is given routinely 5-10 ppm per day. However, if the plankton is thin/little, it is best to grow the plankton first until it is stable.
Meanwhile, if the alkalinity is low because the soil is acidic/peat, do sufficient drying and liming during land preparation and cultivation as well as regular dolomite application to maintain plankton stability, as much as 5-10 ppm per day.
7. TOM (Total Organic Matter) or Organic Materials
Increased organic matter due to plankton drop, overfeeding, and/or shrimp waste can trigger the growth of vibrio bacteria, algae blooms and high TAN and phosphate content.
If the TOM is high due to plankton drop, then do a siphon to get rid of the dead plankton that has settled as soon as possible. Meanwhile, if there are indications overfeeding, do siphon, reduce feed, and water dilution.
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
Biological Parameters
Biological parameters consist of total vibrio (TVC), total bacteria (TBC) and plankton. Following are some of the common constraints and causes found in each parameter:
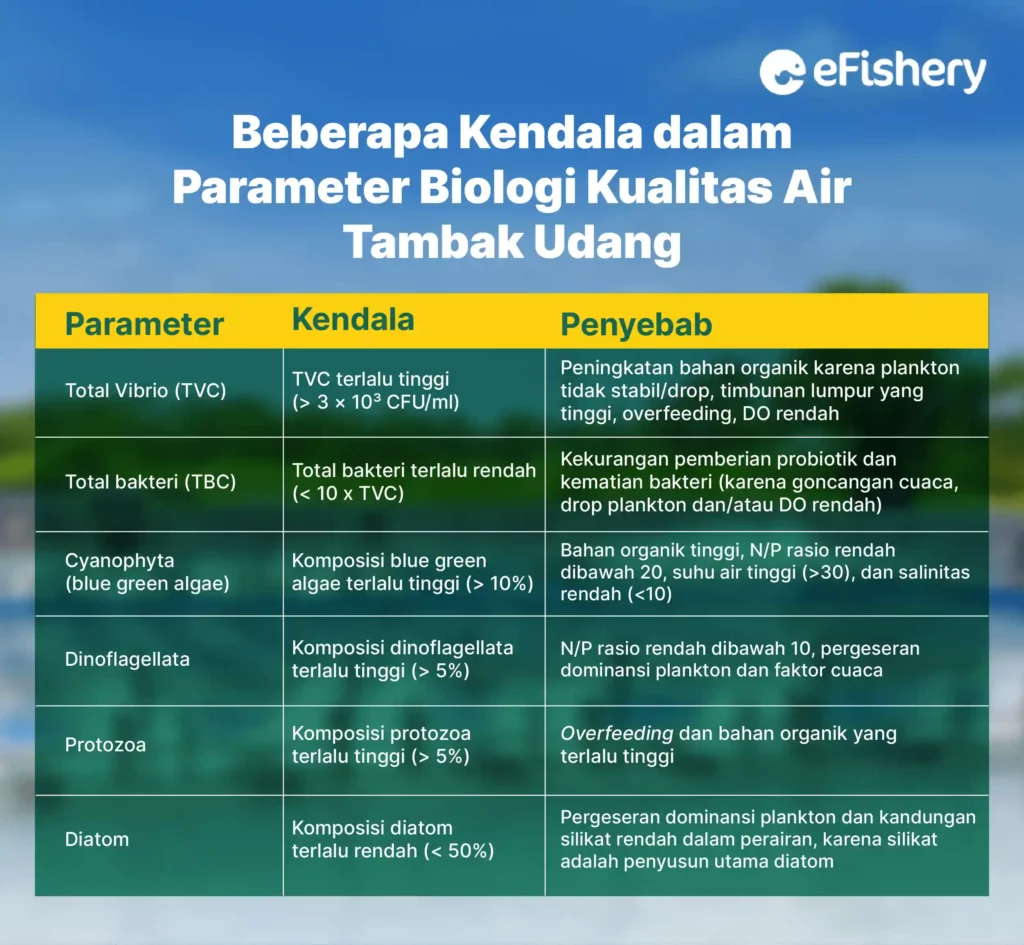
1.Total Vibrios (TVC)
If the total vibrio (TVC) is too high > 3 × 10³ CFU/ml, then give probiotics as soon as possible for protection against vibrio, feed control and cleaning the pond bottom with a siphon and central drain.
If there is an indication of plankton drop, throw away the dead plankton that has settled as soon as possible, then apply 5-10 ppm of captan then spread decomposer probiotics. Besides that, grow plankton again and keep it stable.
2. Total Bacteria (TB)
If the bacteria are too low <10 x TVC, then give probiotics based bacillus subtilis, do plankton growth again and maintain its stability.
3. Cyanophyta (blue-green algae)
If composition blue-green algae too high (> 10%), you can do the following:
- If there is a plankton drop, remove dead plankton that has settled and klekap on the surface as soon as possible and do siphon to reduce organic matter regularly.
- Apply fertilization (especially N fertilizer) to increase the N/P ratio.
- Chemical treatment with Aqualisan 0.5-1.5 ppm to erode BGA. The application was carried out during the day when the water temperature was high and BGA rose to the surface, so it hit the spot. The optimal dose must be adjusted to the type of pond and other water quality parameter conditions.
4. Dinoflagellates
If the composition of the dinoflagellates is too high (> 5%), farmers can closely monitor the feed to ensure that no overfeeding. In addition, you can siphon regularly to reduce organic matter.
5. Protozoa
If the protozoa composition is too high (> 5%), lMonitor the feed strictly to ensure that overfeeding does not occur and carry out siphoning regularly to reduce organic matter.
6. Diatoms
If the diatom composition is too low (< 50%), it is recommended to do this treatments in pool water with silicate (during the maintenance phase) because silicate is the main constituent of diatoms. treatment this is to encourage the growth of diatoms and heterotrophic bacteria as well as maintain the balance of microorganisms in the pond.
Water quality that is not optimal can cause shrimp to experience stress and lead to death if not treated immediately. Therefore, it is important to maintain water quality every day to keep the levels in the optimal range.
Rawat Kualitas Air Tambak dengan Konsultasi ke Ahli Budidaya
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
The quality of shrimp pond water needs to be maintained properly so that it remains in the optimal range according to the needs of the shrimp. Water quality is maintained so that shrimp are not easily stressed, plankton growth remains optimal and processes that occur in the water continue to run well. To simplify and maximize water quality management, you can consult via Cultivation Consultation inside the app eFarm.
eFarm is a shrimp pond management application that is equipped with features that can help the shrimp cultivation process. One of the features it has eFarm is Cultivation Consultation. Through this feature, you can consult about shrimp issues, which will be answered by an aquaculture expert. In addition, you can access it for free.
So what are you waiting for? Consult cultivation problems easily together eFarm.

Eko Afriantoro - Praktisi Budidaya Udang
Eko berpengalaman sebagai praktisi budidaya udang sejak tahun 2013 yang kini menjadi Farm Lead Research & Development (R&D) Shrimp eFishery.
Questions Regarding Parameters of Water Quality in Shrimp Ponds
Water quality requirements for shrimp farming include physical parameters (temperature, brightness, and water color), chemical (pH, DO, salinity, ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, and alkalinity), and biology (TVC, TBC, and plankton).
Pond water quality parameters consist of physical, chemical and biological parameters. The parameters of safe water quality for shrimp farming are not exceeding the minimum and maximum limits that have been determined.
- Akmal, Y., R. Humairani, M. Muliari and I. Zulfahmi. 2021. Increased Economic Value in the Sea Mina Cultivation Group of Vaname Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Bireuen District, Aceh. Solma's Journal. 10(02): 275-286.
- Jumraeni, A. Khaeriyah, Burhanuddin and A. Anwar. 2020. The effect of the disposal model on the accumulation of organic matter in intensive vannamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) ponds. Octopus: Journal of Fisheries Science. 9(1): 11-18
- Ningsih, A., Sulistiono, STM Sulthoniyah. 2021. Field work practice of water quality management in vanamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultivation at PT. Surya Windu Kartika, Bomo Village, Rogojampi District, Banyuwangi Regency. Journal of Fisheries and Marine Sciences. 3(1): 15-25.
- Sahrijanna, A and Sahabuddin. 2014. Study of water quality in the cultivation of vannamei shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) with a feed rotation system in intensive ponds. Proceedings of the Aquaculture Technology Innovation Forum. 313-319
- Suriawan, A., S. Efendi, S. Asmoro and J. Wiyana. 2019. Vaname shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) cultivation system in HDPE ponds with high salinity underground water sources in Pasuruan Regency. Journal of Brackish and Marine Aquaculture Engineering. 5-14
