Artikel Ini Telah Direview Oleh:

Laksono Radityo
Praktisi Budidaya Udang
WWTP (Wastewater Treatment Plant) has an important role in shrimp farming. WWTP for shrimp ponds functions to manage waste generated from ponds before the water returns to the environment. The waste generated from shrimp farming can cause water pollution, if you don't manage it properly.
WWTP for shrimp ponds is very important, isn't it? Therefore, you need to understand the definition, function, and method of making WWTP. Come on, see here!
Principles of Pond Wastewater Treatment
The principle of shrimp pond wastewater treatment is to improve water quality so that when it is disposed of it does not pollute the environment, especially public waters. Improving the quality of wastewater is carried out by:
- Separating solids from wastewater
- Reducing pollutants from wastewater, so that the quality of WWTP processing results does not pollute the surrounding environment.
Characteristics of Pond Wastewater

Pond water waste contains high organic matter particles, consisting of shrimp faeces, uneaten feed, shrimp carapace, dead plankton that settles on the bottom of the pond, as well as high N and P content which can increase water fertility.
Shrimp pond wastewater contains several water quality parameters with quite high levels, such as Biological Oxygen Demands (BOD), Total Suspended Solids (TSS), Total Organic, turbidity, Total Nitrogen (TN), and Total Phosphates (TP).
Shrimp pond wastewater super intensive with a stocking density of 750-1,250 fish/㎡, containing TSS 798-923 mg/L, total organic 81.22-88.64 mg/L, TN 9.83-14.42 mg/L, and TP 7.87- 11.87mg/L. The sediment that is formed reaches 18.2-21.9 tonnes/0.1 ha/shrimp production cycle.
The increase in solid waste in the aquaculture system must be prevented, because it will cause a decrease in dissolved oxygen and increase ammonia levels. This is because the process of decomposition of organic matter is toxic to shrimp. Therefore, disposal of sludge needs to be done periodically.
WWTP definition
WWTP is a water structure that functions to treat waste water originating from shrimp enlargement activities. The function of WWTP is to process waste in 3 stages, namely:
- Physical Stage, serves to reduce suspended solids in waste.
- Biology Stage, serves to decompose organic waste in water.
- Chemical Stage, serves to kill disease-carrying microorganisms.

For the legal basis of IPAL, you can refer to:
- Law Number 5 of 1990 concerning Conservation of Living Natural Resources and Ecosystems.
- Law Number 32 of 2009 concerning Environmental Protection and Management.
- Government Regulation Number 82 of 2001 concerning Water Quality Management and Water Pollution Control.
- Government Regulation Number 27 of 2012 concerning Environmental Permits.
- Minister of Environment Regulation Number 5 of 2014 concerning Wastewater Quality Standards.
Factors Influencing WWTP Design
WWTP design in shrimp ponds is influenced by several factors, as follows:
- Waste Water Volume
WWTP design is influenced by the volume of wastewater produced. The volume of water is used to determine the capacity of the wastewater treatment unit. If the volume of wastewater is large, the capacity of the treatment unit must be large to accommodate the wastewater.
- Wastewater Flow Rate
The velocity of wastewater flow greatly affects the sedimentation process. The sedimentation process can be optimal if the water flow rate is ≤ 20 m/sec.
- Availability of Land or Space
The amount of land for WWTP is determined by several factors, such as the volume of wastewater to be treated and the variety of waste water pollution materials.
- Cost Availability
Costs incurred in making WWTP include the construction, operation and maintenance of WWTP. The cost depends on the technology and equipment used.
- Other Benefits
WWTP can generate profits from processing results, both in the form of solids and liquids. Solids from the sedimentation process can be used as plant fertilizer. However, these solids contain a high salt content, preferably the use of fertilizer from sedimentation sludge a maximum of 30% of the total used.
WWTP wastewater can be used as inoculation material to grow plankton or natural feed in ponds. In addition, the organisms in the WWTP can be used as a biofilter in the waste treatment process.
WWTP SOP
The following is the operational standard for the use of WWTP that you need to know:
1. Design and Build
a. Design of WWTP Location for Shrimp Growing
The following is a recommended Shrimp Growing WWTP location:
- Not too far from the maintenance location.
- Not far from the neighborhood sewer.
- Locations that are free of contamination or not polluted.
- Make sure that the WWTP disposal is far enough away from the water source.
After you know the recommended WWTP location, you also need to know the WWTP building construction which consists of the building structure and WWTP material requirements, as follows:
b. WWTP Building Structure
- WWTP building construction can be made of soil, concrete, or plastic lining ponds. The WWTP structure must be strong, sturdy and stable to withstand the waste load.
- The WWTP structure is designed to be able to withstand the waste load when the soil shifts due to earthquakes, wind, the effects of corrosion, fungi, and so on.
- Maintenance and inspection of WWTP building functions must be carried out periodically.
c. Material Requirements
- Structural materials used must comply with technical standards (SNI) and safety requirements.
- Materials that are made or mixed must comply with standard procedures for the purposes of making WWTP.
In designing the WWTP for shrimp ponds, you need to know the required land area or the building capacity of the WWTP. The ratio of WWTP volume and water volume can be adjusted according to the shrimp enlargement technology, as follows:
- The volume of WWTP plots in semi-intensive and intensive technology is a minimum of 20% of the total volume of grow-out media water with a minimum residence time of 2 days.
- The volume of WWTP plots on super-intensive technology is at least 30% of the total volume of water of the grow-out medium with a minimum residence time of 5 days.
- If the procurement of WWTP plots is on narrow land, while the volume of wastewater for growing shrimp is large, then higher technological inputs are required and require additional costs for WWTP equipment.
- The volume of WWTP plots greatly affects the discharge of water from each pond. The more ponds and the stocking density of shrimp, the greater the volume of WWTP required.
2. WWTP installation
a. Main Facilities
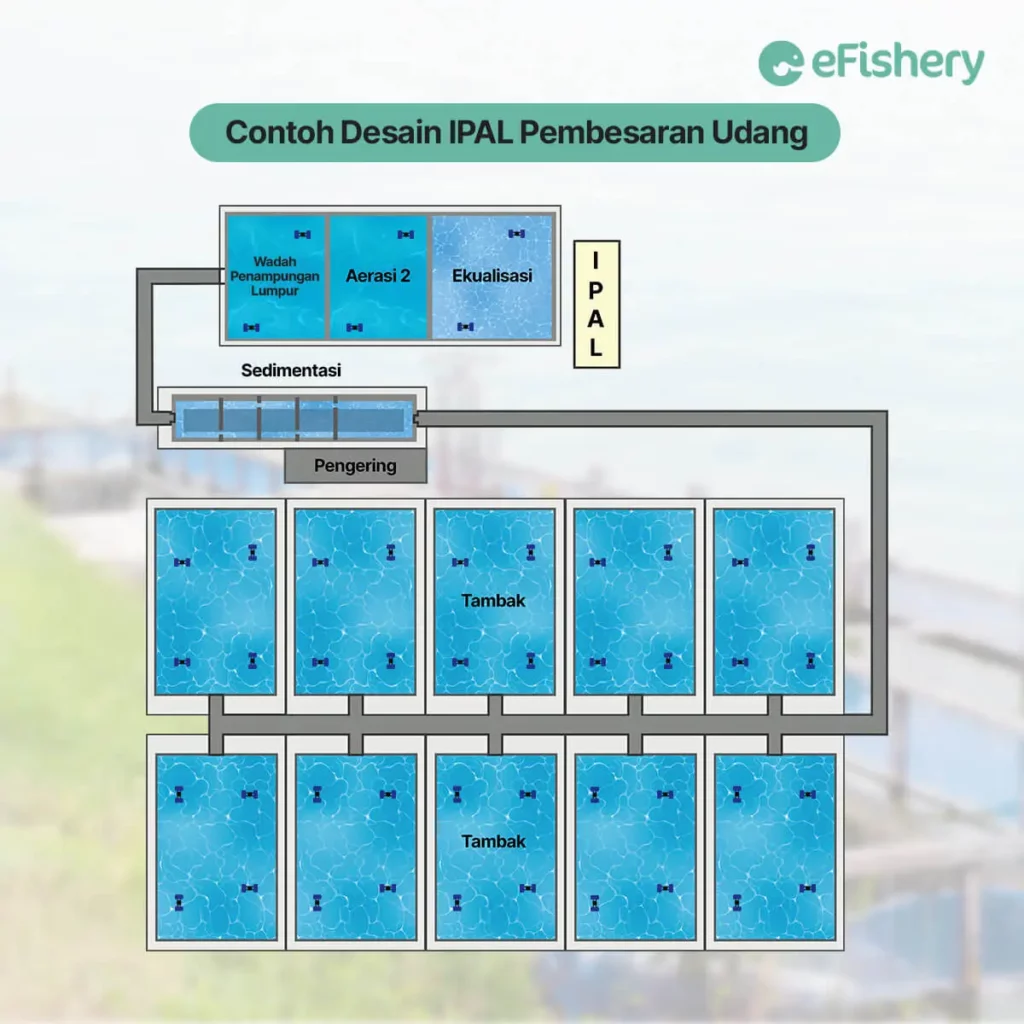
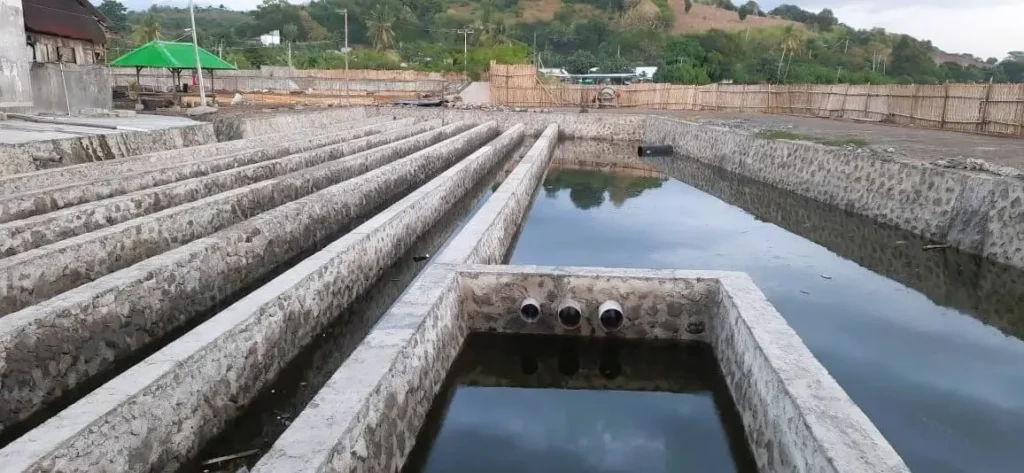
WWTP for shrimp ponds has the following main facilities:
- Sedimentation Pool
Sedimentation ponds are the first stage of processing physically to reduce suspended solids content through a settling process. Generally, these ponds are designed to be partitioned in order to slow down the flow of waste water and extend the path or time for the flow of water, thereby spurring the process of settling solid particles.
- Aeration Pool
An aeration pond is a waste treatment unit equipped with an aeration system. The goal is to increase dissolved oxygen levels, reduce BOD, increase pH in wastewater, and remove CO2 and H2S, as well as other dissolved gases.
- Equalization Pool
The equalization pond is a pond for holding waste water in the final stage. Usually, seaweed and fish are reared in equalization ponds which function as bioindicators. Seaweed will absorb nutrients and convert into harvestable biomass. Then, the remaining nutrients will spur the growth of plankton as a natural food for fish.
The equalization pond also functions to determine whether the water produced by WWTP is suitable for living organisms. If the fish in this pond can live well, then the WWTP treated water is categorized as good. On the other hand, if the fish in this pond die, the WWTP treated water is categorized as bad.
- Sludge Storage Container
The mud storage container is a place for collecting sludge from the sedimentation pond and functions to dry the sludge or sediment.
b. Equipment
The following is the equipment in the Shrimp Enlargement WWTP, as follows:
1) Separator Equipment
Some of the separation equipment that can be used, as follows:
- Bar Screen (separator between liquid and solid)
- communitor (solid crusher)
- Compactor (compacter)
- Grit Removal (sediment or solids collection container)
- clarifier (a tool or container for settling with a centrifugal system)
- Thickener (solution thickener)
2) Equipment for Biological Processes (Biological Treatment)
This equipment can be:
- aerators
- Mill
- Batchreactors (container for mixing)
- blowers
- Plastic Media
- Rotating Biological Contactors (container maintenance of microorganisms)
3) Electrical Equipment
The types of electrical equipment needed in WWTP include pumps, mixers, aerator, scraper, thickener, And plan control.
3. WWTP Operations
a. IPAL operation
In operating WWTP, you need mechanical and electrical system readiness in good condition. The following is the IPAL operation flow:
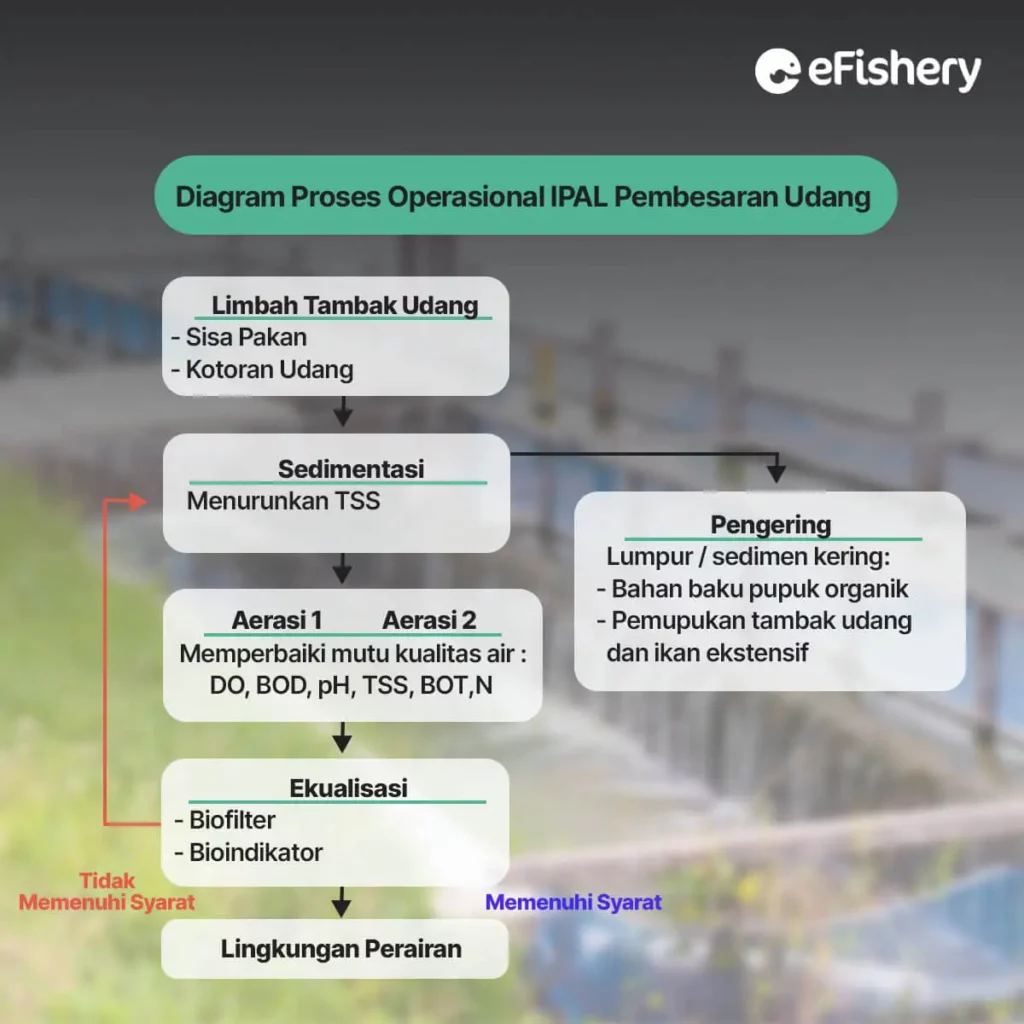
Wastewater from shrimp ponds is channeled into a sedimentation pond equipped with a filter to catch coarse particles. Here's how to drain wastewater:
- Gravity system, this system is used to drain wastewater from high places to lower WWTP channels.
- Pressurized system, if the WWTP is located higher than the sewerage channel, the wastewater is collected first, then pumped to the WWTP.
- The combined system combines gravity flow and pumping.
Shrimp rearing wastewater that has passed through the sedimentation pond will flow to the aeration pond 1, then flow to the aeration pond 2 to improve water quality conditions. After that, the wastewater is channeled into the equalization pond before being discharged into the aquatic environment. If the water quality of the equalization pond has not achieved the desired results, it is necessary to pump it back into the aeration pond in order to repeat the biofiltration process.
b. WWTP treatment
The following are some things that need to be considered to maintain the condition of the WWTP:
- Make sure that no solid waste enters the WWTP.
- Make sure that no factory waste enters the WWTP.
- Clean the sedimentation pond filter regularly to prevent clogging.
- Avoid the entry of toxic chemicals that can interfere with microbial growth in the aeration pond.
- Drain the sludge in the settling pond and equalize it periodically.
- Perform routine maintenance on the slurry pump, waste water pump, and blowers air according to the operating instructions.
- Perform regular and periodic WWTP maintenance in each pond. Keep in mind, the more ponds and the higher the stocking density, the more water recirculation is carried out in each pond.
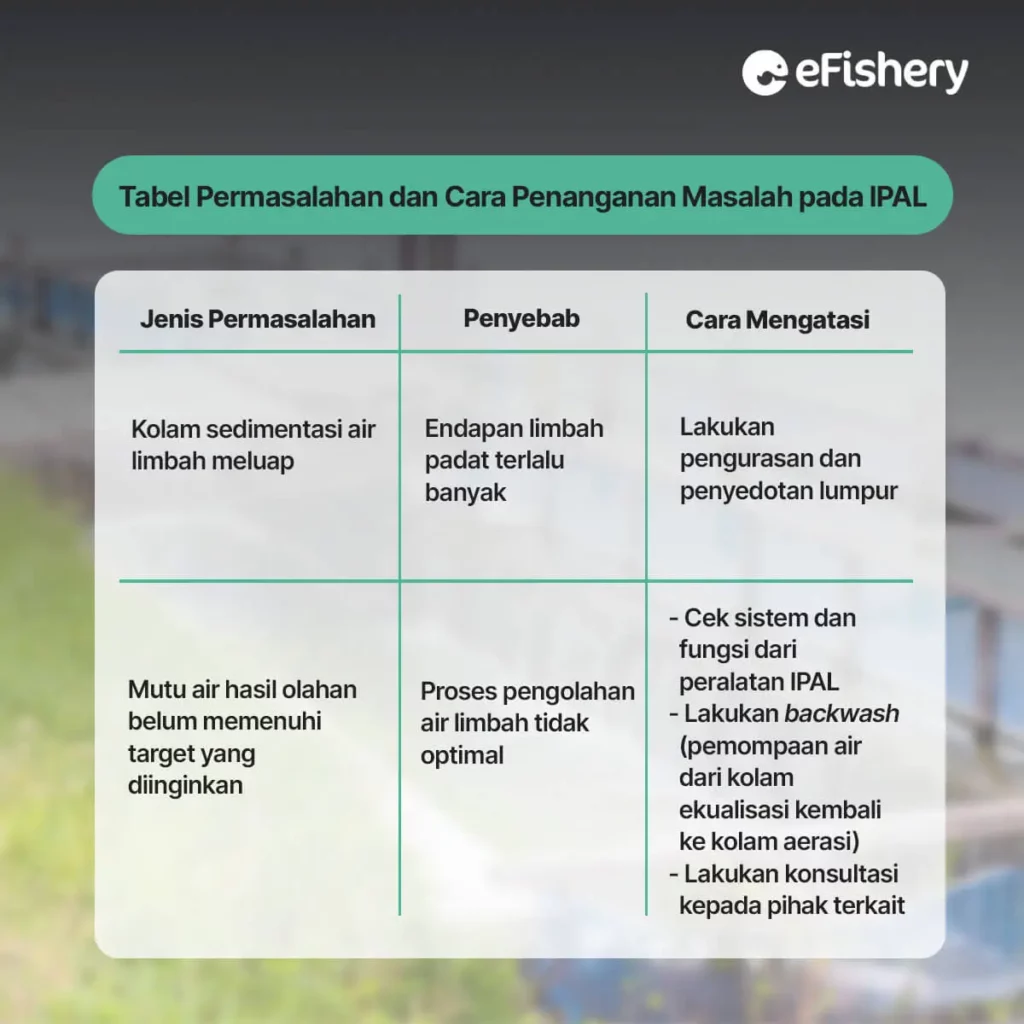
c. Problems and Ways of Handling
The following are the problems and how to handle them in WWTP operations:
d. Implementation of K3 for WWTP Executors
Wastewater management must be monitored by Occupational Health and Safety (K3) for WWTP implementers, both directly and indirectly related to wastewater as a whole. The following are several aspects of K3 implementation guarantees that must be fulfilled so that WWTP implementers can work properly:
- Complete K3 equipment for use when working.
- Health insurance for executors.
Risks Faced If the Pond Does Not Have WWTP
Shrimp pond wastewater contains many viruses and pathogenic microorganisms originating from faeces and leftover feed at the bottom of the pond. If you allow this waste to be dumped in rivers and seas, it will be detrimental to the environment in the long term.
The following are the risks faced if the pond does not have an WWTP:
- Expansion of siltation zones in estuaries and coastal waters.
- Indication of increasing concentration of organic matter in seawater.
- Layer formation anoxia (low oxygen) and euxinia (high sulfide) in the sea.
- Bacterial colony Vibrio parahaemolyticus has high resistance to antibiotics, probiotics, and disinfectants.
- 70% toxin was detected in the mud, while 30% in water and other substrates were wild crustaceans.
Apart from being detrimental to the environment in the long term, the risk is that if you do not have an WWTP in the shrimp farming business, your business will receive a warning for imposition of administrative fines and be temporarily suspended by the KKP, according to the applicable legal process.
This is intended so that business actors can improve and complete business permits, apply CBIB (Good Fish Cultivation Practices), and WWTP (Wastewater Treatment Plant) according to specified standards.
Come on, Consult the Making of WWTP with Experts at the eFarm Cultivation Consultation!
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
Itu dia definisi, fungsi, dan cara pembuatan IPAL pada tambak udang. Dalam setiap budidaya, kadar polutan tergantung pada lama pemeliharaan, padat tebar udang, substrat dasar kolam, dan konstruksi tambak.
Saat memulai budidaya udang, tak dipungkiri Petambak perlu mempersiapkan seluruh kebutuhan budidaya agar berjalan dengan maksimal, salah satunya adalah IPAL.
If you have searched for information about WWTP but don't feel like you have gotten the best answer, then you can consult through the feature Cultivation Consultation in eFarm. You have the opportunity to ask questions and discuss directly with Aquaculture experts and professional shrimp farmers for free.
Very helpful right? Come on, hurry up downloads eFarm now and take advantage of its various features, it's free!

Laksono Radityo - Praktisi Budidaya Udang
Berpengalaman sebagai asisten riset perikanan dan teknisi tambak udang. Saat ini aktif sebagai Technical Support Online di eFishery
Questions Regarding Shrimp Pond WWTP
WWTP for shrimp ponds is a water structure that functions to treat waste water originating from shrimp enlargement activities, before the water returns to the aquatic environment.
Shrimp pond waste is very dangerous because it can disrupt ecosystems around ponds, such as siltation of river estuaries and coastal waters, increased concentrations of organic matter in the sea, and the bacteria produced have high resistance to antibiotics, probiotics and disinfectants.
- Marine and Fisheries Ministry. 2019. Technical Instructions for Shrimp Growing Wastewater Treatment Plant. 30 pp.
- Marine and Fisheries Ministry. 2021. Shrimp Pond WWTP: A Practical Solution for Pond Waste Management. Indonesian Shrimp Forum Webinar
- Shah R, Fahrur M, Suryanto H, and Makmur. 2017. Performance of the Superintensive Pond Wastewater Processing Installation. Aquaculture Media. 12(2): 95-103
