Artikel Ini Telah Direview Oleh:

Syavin Pristiwayuning
Penulis Makalah Ilmiah Perikanan
Hello Mister / Ms Shooters! Do you want to increase the productivity of vannamei shrimp farming? If so, traditional plus vannamei shrimp farming is worth a try. So, how can traditional vannamei shrimp cultivation plus increase cultivation productivity? Find out the complete reason along with the method and analysis of its cultivation in this article, come on!
The Potential of Traditional Shrimp Cultivation Plus
To achieve the 5-year program (2020-2024) of the Ministry of Maritime Affairs and Fisheries (KKP) which aims to increase 250% of Indonesian shrimp exports, it is necessary to increase the export value above 20% per year. Therefore, a shortcut is needed so that increased shrimp production can be achieved quickly. One way that can be done is to transform traditional shrimp ponds into traditional plus.
This strategy is quite prospective because when viewed from the area, traditional ponds have the largest proportion of land area compared to other cultivation systems. There are about 300 thousand hectares of traditional ponds in Indonesia. However, its productivity is still very low, only around 500 kg/ha/year. This is because traditional ponds only rely on natural feed with low shrimp stocking densities. If this productivity can be increased up to 1-2 tons/ha/year with traditional plus cultivation, there will be a significant increase in production.
The concept of traditional-plus ponds is not only to increase the productivity of traditional systems, but also to revitalize stalled intensive/semi-intensive ponds. So that the thousands of ponds can be re-operated through the traditional-plus system with relatively lower costs and risks.
Differences in Traditional & Traditional Shrimp Cultivation Systems Plus

Traditional
Cultivating vannamei shrimp using the traditional system is only suitable for low fry stocking densities (1-5 individuals/m2). This is because the cultivation of traditional systems only relies on natural feed and does not use artificial feed at all. In addition, shrimp farming with traditional systems also does not use aerators to increase the oxygen content in the water. Therefore, traditional systems are less able to increase cultivation productivity.
Traditional Plus
Unlike the traditional system, the traditional plus cultivation system can increase productivity by adding stocking density (8 individuals/m2), pellets, provision of aerators, and other appropriate technologies. Besides being able to increase productivity, the traditional plus system can also create sustainable (environmentally friendly) shrimp farming and increase income and the welfare of farmers. Even though the productivity is high, the cost of cultivating the traditional plus system is relatively small and still considers environmental sustainability.
Traditional Shrimp Cultivation Methods Plus

A. Pond Preparation
1. Basic Soil Preparation and Map Improvement
Extensive (traditional) pond soil types generally consist of mature peat and acid sulphate soil (TSM), which are classified as swamp areas. Usually, acid sulfate soils contain pyrite compounds which can increase the degree of soil acidity (decrease in pH) when it encounters air and high organic matter content. To fix it, remediation and reduction of toxic elements or compounds in the soil are needed.
To increase the productivity of traditional ponds, it is necessary to remove bottom silt, fill bunds, and repair sluice gates in order to increase production in accordance with traditional plus shrimp farming. Next, carry out tillage using a hand tractor or a hoe to a depth of 0.2 m so that the surface area of the soil increases and the oxidation process becomes better. However, this stage is only carried out if the cultivation cycle is carried out during the dry season. This stage is carried out for 2 weeks when the sun is hot or until the pond is completely dry. If so, soak the pond for 1 week and wash it to dissolve the toxic elements present. The process is repeated 2 or 3 times until the soil conditions get better.
If the cultivation cycle is carried out during the rainy season, the preparation of the subgrade is only carried out by removing the bottom silt from the surrounding canal, repairing the bunds, and drying it. Subgrade drying is carried out until the soil is cracked, approximately 2-3 weeks. The redox potential of the pond bottom soil when dry should be at least +50 mV.
2. Pest Eradication
This stage can be done by reducing wild fish that were previously in the pond with saponins of 15-20 ppm (7.5-10 kg/ha) with 5 cm of water in the pond.
3. Liming

Liming aims to increase soil and water pH and reduce nutrients that cause soil acidity. The types of lime used in ponds are carbonate lime, oxide lime, and hydrated lime. In the traditional plus vannamei shrimp farming technology, liming can be done using carbonate lime (agricultural lime) during soil processing and after washing the pond with doses.
If the subgrade conditions stink, use lime oxide, and to stimulate the growth of natural feed, use dolomite lime. Dolomitic lime is also most effectively used as follow-up lime (3-5 ppm). But keep in mind, lime will not react if the soil is very dry, therefore lime is applied to pond bottom soil which is moist but dry enough for people to walk on.
4. Fertilization
In traditional plus vannamei shrimp farming, in addition to commercial feed, shrimp also need to be given natural food (plankton) which will only grow through the fertilization process. Generally, traditional ponds have acid sulphate soil conditions. So to improve the traditional vannamei shrimp farming technology to become traditional plus, fertilization with organic and inorganic fertilizers is needed for soil fertility in acid sulfate ponds.
5. Water filling
Filling with water is carried out after all the pond bottom preparations have been completed and water is gradually added to the pond. The ponds that have been filled with water are then left for 2-3 weeks until conditions are completely ready for spreading shrimp fry. The water level in the enlargement plot is attempted to be ≥1.0m.
B. Spreading fry
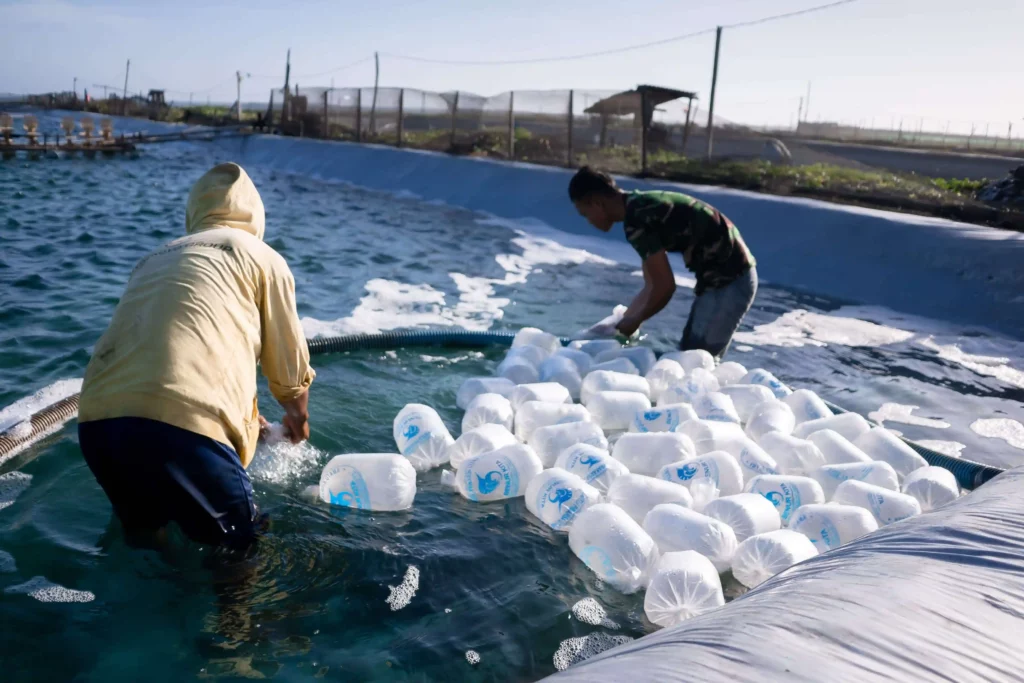

Spreading of vannamei shrimp fry is carried out after the plankton grows well (7-10 days) after accumulation. You can get shrimp fry from hatchery who have obtained a pathogen-free recommendation or Specific Pathogen Free (SPF).
Vannamei fry that are ready for cultivation are fry with a PL size of 10-12 (initial weight 0.001 g/head) or have perfect gill organs, uniform size, clear body, clearly visible intestines, and can swim against the current.
Before stocking the fry, acclimatize to the temperature by floating the bag containing the fry in the pond. In addition to temperature acclimatization, salinity acclimatization is also required by adding pond water little by little to the bag for 15-20 minutes. Next, tilt the fry bag and the vannamei shrimp fry will come out by themselves. The spreading of vannamei fry is carried out in the morning or evening with a stocking density of 8 individuals/m².
C. Maintenance

During maintenance, monitor water quality (temperature, salinity, transparency, pH, depth and oxygen) every day. In addition, apply 5-10% of urea and TSP every week from the initial amount of fertilizer. Then, to maintain the stability of the plankton in the pond, use the fermented probiotics once a week. Carry out subsequent liming with super dolomite if the pH fluctuates.
Artificial feed is given on the 30th day or a maximum of the 40th day when the support for natural food (plankton) is reduced or the growth of shrimp begins to slow down. The feed dose given was 5-2% from shrimp biomass with a frequency of 3 times/day, namely 30% at 7.00 and 16.00 and 40% at 22.00.
The first water change was carried out after the shrimp were 30 or 40 days old with a replacement volume of 10% of the total volume. Whereas in the following month until harvest, the volume of water replacement is increased to reach 15-20% in each high tide period. Before the age of maintenance reaches 60 days, the addition of water is only done as much as the amount of water lost due to evaporation or seepage. Decent water quality for vannamei enlargement is optimal salinity 10-25 ppt (tolerance 50 ppt), temperature 28-31°C, oxygen >4 ppm, ammonia <0.1ppm, pH 7.5-8.2, and H²S < 0.003 ppm.
D. Harvest
Harvesting is done by considering the price, growth and health aspects of the shrimp. Harvesting is done after 100-110 days of maintenance. Before harvesting, apply calcification with dolomite lime as much as 80 kg/ha (if the pond water level is 1m) and maintain the water level (no water changes) for 2-4 days so that the shrimp do not change their skin during harvest.
After that, prepare harvesting equipment such as harvesting baskets, nets installed at the water gates, throwing nets, synthetic cork, buckets, basins, and lighting lamps. When harvesting, lower the volume of water and catch the shrimp with nets at the same time. Harvesting should be done at night to reduce the risk of damage to shrimp quality, because shrimp are very sensitive to sunlight. The caught prawns must also be washed and then soaked in ice for further transport coldstorage.
Analysis of Traditional Shrimp Cultivation Business Plus
After knowing the potential and methods of traditional plus system shrimp farming, it's time for you to know about capital analysis simulations and their benefits. The following is an analysis of the traditional plus vannamei shrimp farming business with a total fry of 80,000 heads/ha in Day of Cultivation (DOC) or 105 days of cultivation.
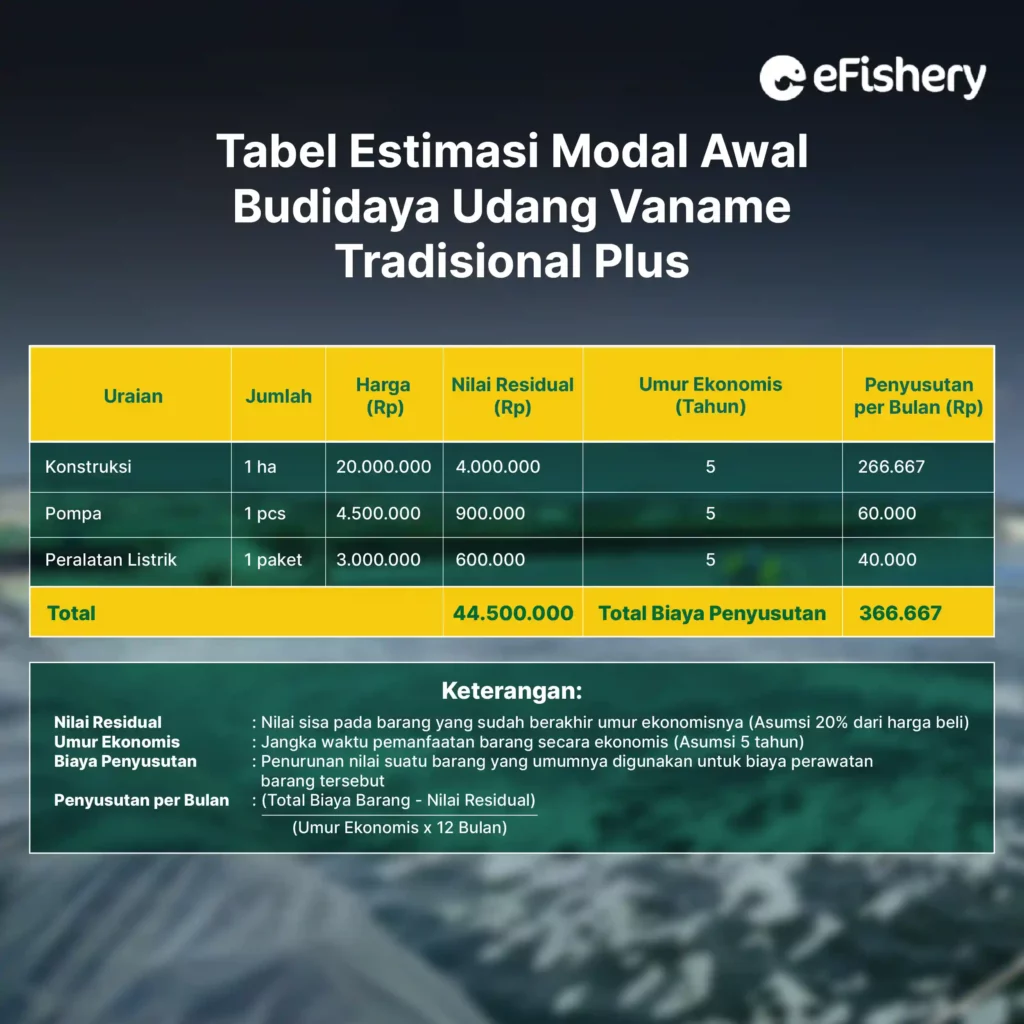
Apart from the initial capital, there are also operational costs that you have to spend during the cultivation cycle. To find out how much it costs to cultivate traditional vaname shrimp plus for 1 cycle, here are the details:
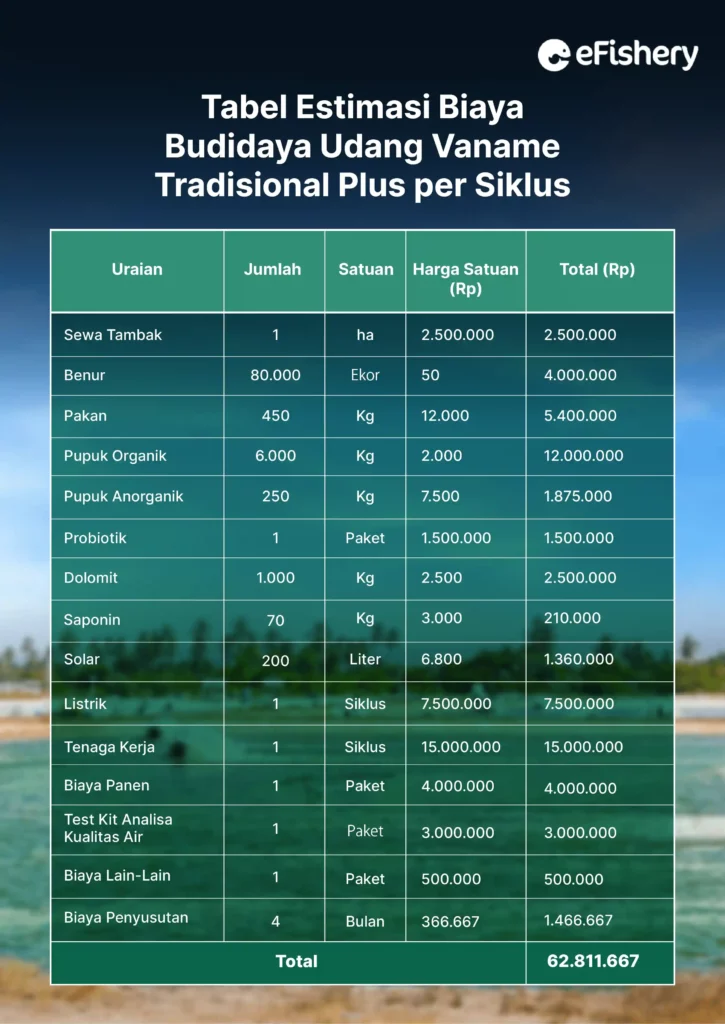
*The table above is only an estimated calculation. Prices listed can change at any time and adjust to market prices
If totaled, the total cost required in the cultivation of the traditional system plus per cycle is IDR 62,811,667.
To calculate profits, you need numbers survival rates (SR) shrimp at harvest. If at harvest the shrimp SR number is 85%, then from 80,000 shrimp, you can harvest 68,000 shrimp. Then, if you harvest shrimp with the size 50 head/kg, Mr / Ms will get 1360 kg shrimp.
The selling price of shrimp in each city is different. To take a real example, let's use the price per kilo of vannamei shrimp in Banten Province in 2022, namely IDR 70,000. If you sell vannamei shrimp for IDR 70,000 per kilo, in 1 cultivation cycle You will get a total receipt of IDR 95,200,000.
Means, gain per cycle what you can get is:
IDR 95,200,000 – IDR 62,811,667
= IDR 32,388,333
Get Complete Tips for Traditional Plus Shrimp Cultivation at eFishery
Need Help Regarding Shrimp Cultivation Business?
Fill in your personal data in the following form. Our team will immediately contact you via the number cellphone attached. Make sure the data entered is correct.
How are you, sir/madam? Are you interested in the benefits offered by traditional plus shrimp farming after reading this article? If so, you should first consult with a shrimp farming expert eFishery through features Cultivation Consultation in app eFarm. Besides being able to consult directly with shrimp farming experts, in the application eFarm You can also find other information about shrimp farming. Downloads application eFarm on the Google Play Store!
Fill out the form below to consult at Cultivation Consultation!

Syavin Pristiwayuning - Penulis Makalah Ilmiah Perikanan
Berpengalaman sebagai asisten koordinator pelatihan teknisi pada tahun 2020 dan saat ini aktif sebagai Technical Support Online di eFishery
- https://bppbapmaros.kkp.go.id/wp-content/uploads/Pa.-Dayat-Budidaya-udang-vaname-Rekomtek-2015.pdf
- http://ejournal-balitbang.kkp.go.id/index.php/ma/article/viewFile/2826/2328
- https://www.academia.edu/14702903/BUDIDAYA_UDANG_VANNAMEI_LITOPENAEUS_VANNAMEI_POLA_TRADISIONAL_PLUS
- https://www.minapoli.com/info/budidaya-tradisional-plus-sebagai-jalan-pintas-peningkatan-produksi-udang-nasional
